Barogenic perforation of the esophagus: An unusual manifestation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.758Keywords:
Esophageal barotrauma, Spontaneous esophageal perforation, Boerhaave síndromeAbstract
Introduction: Typically, when esophageal perforation secondary to barotrauma is mentioned as the causal pathophysiological mechanism of perforation, the literature refers to spontaneous esophageal perforation or Boerhaave syndrome as an entity. It involves the longitudinal and transmural rupture of the esophagus (previously healthy) secondary to an abrupt increase in intraluminal esophageal pressure, frequently triggered during vomiting. However, in the medical literature, some reports list mechanisms of barotrauma other than this entity.
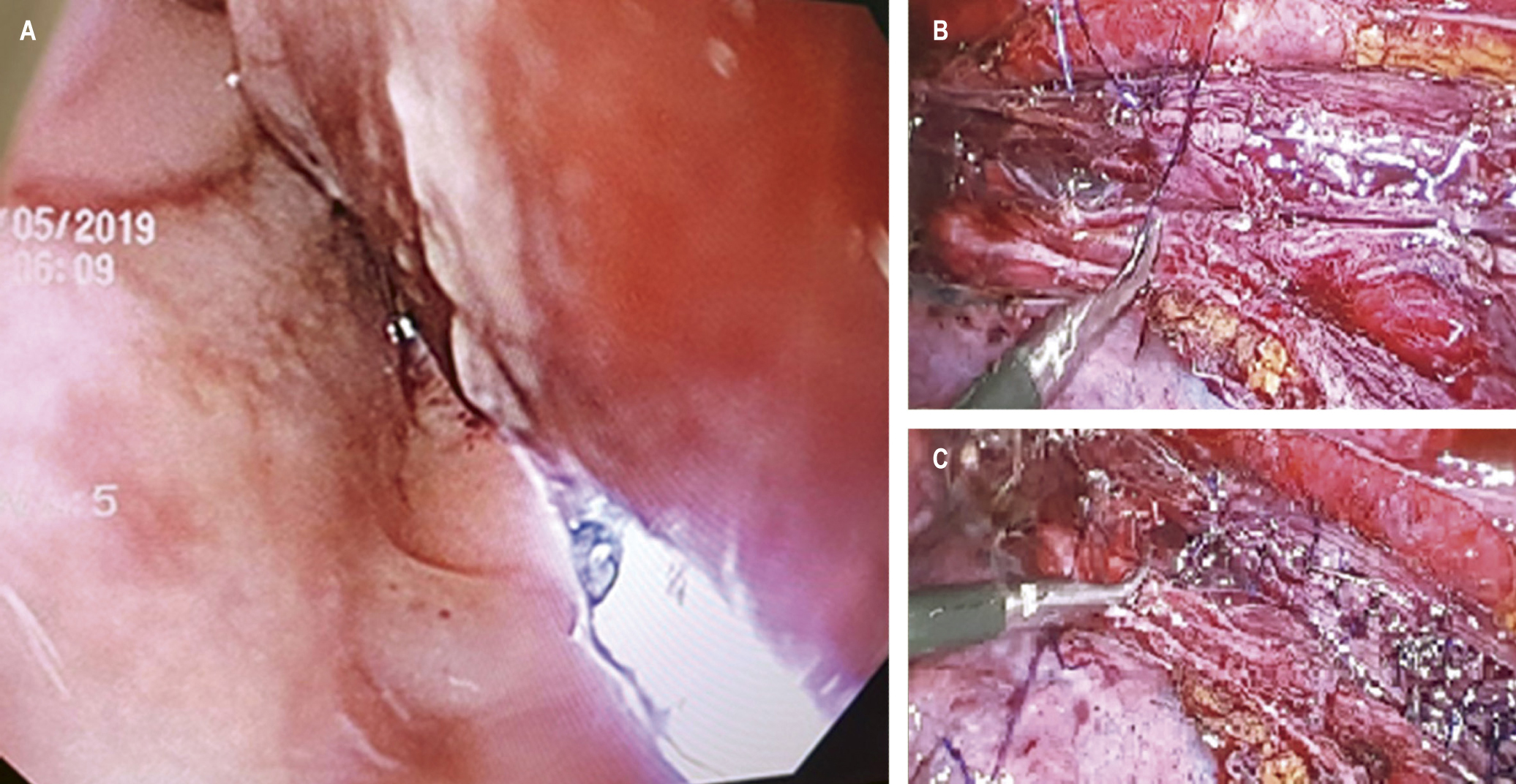
Case report: A 64-year-old female patient with a history of surgically managed gastric adenocarcinoma (total gastrectomy and esophagoenteral anastomosis) presented with stenosis of the esophagojejunal anastomosis, which required an endoscopic dilatation protocol with a CRETM balloon. The third session of endoscopic dilation was held; in removing the endoscope, we identified a deep esophageal laceration with a 4 cm long perforation at the level of the middle esophagus (8 cm proximal to the dilated anastomosis), suspecting the mechanism of barotrauma as the causal agent. She required urgent transfer to the operating room, where we performed thoracoscopic esophagectomy, broad-spectrum empiric antimicrobial coverage, and enteral nutrition by advanced tube during in-hospital surveillance. The control esophagram at seven days showed a small leak over the anastomotic area, which was managed conservatively. Imaging control at 14 days showed a decrease in the size of the leak, with good evolution and tolerance to the oral route. The patient was later discharged.
Downloads
References
Shenfine J, Griffin SM. Oesophageal rupture. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2007;68(2):M18-21. https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2007.68.Sup2.22838
Saxena P, Khashab MA. Endoscopic management of esophageal perforations: Who, when, and how? Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2017;15(1):35-45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11938-017-0117-3
Nirula R. Esophageal perforation. Surg Clin North Am. 2014;94(1):35-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2013.10.003
Kaman L, Iqbal J, Kundil B, Kochhar R. Management of esophageal perforation in adults. Gastroenterology Res. 2010;3(6):235-44. https://doi.org/10.4021/gr263w
Sdralis EIK, Petousis S, Rashid F, Lorenzi B, Charalabopoulos A. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of esophageal perforations: Systematic review. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30(8):1-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/dote/dox013
Paspatis GA, Dumonceau JM, Barthet M, Meisner S, Repici A, Saunders BP, et al. Diagnosis and management of iatrogenic endoscopic perforations: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) position statement. Endoscopy. 2014;46(8):693-711. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1377531
Rokicki M, Rokicki W, Rydel M. Boerhaave’s syndrome- over 290 yrs of surgical experiences. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis. Pol Przegl Chir. 2016;88(6):359-64. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjs-2016-0077
Dinic BR, Ilic G, Rajkovic ST, Stoimenov TJ. Boerhaave syndrome - case report. Sao Paulo Med J. 2017;135(1):71-5. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0095220616
Ekladious A, Tiong MK. Boerhaave syndrome: A common manifestation of a rare disease. Intern Med J. 2018;48(2):222-3. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.13697
Salo J, Sihvo E, Kauppi J, Räsänen J. Boerhaave’s syndrome: lessons learned from 83 cases over three decades. Scand J Surg. 2013;102(4):271-3. https://doi.org/10.1177/1457496913495338
Boerhaave H. Atrocis nec descripti prius, morbi historia. Secundum medicae artis leges conscripta. Ex officina Bontesteniana: Lugduni Batavorum. 1724.
Søreide JA, Viste A. Esophageal perforation: diagnostic work-up and clinical decision-making in the first 24 hours. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2011;19:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-7241-19-66
Van de Louw A, Brocas E, Boiteau R, Perrin-Gachadoat D, Tenaillon A. Esophageal perforation associated with noninvasive ventilation: A case report. Chest. 2002;122(5):1857-8. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.122.5.1857
Park JB, Hwang JJ, Bang SH, Lee SA, Lee WS, Kim YH, et al. Barotraumatic esophageal perforation by explosion of a carbonated drink bottle. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93(1):315-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.06.071
Buntain WL, Lynn HB. Traumatic pneumatic disruption of the esophagus. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1972;63(4):553-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5223(19)41868-0
Lee JK, Lim SC. Barotraumatic perforation of pharyngoesophagus by explosion of a bottle into the mouth. Yonsei Med J. 2005;46(5):724-8. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2005.46.5.724
Gubbins GP, Nensey YM, Schubert TT, Batra SK. Barogenic perforation of the esophagus distal to a stricture after endoscopy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1990;12(3):310-2. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-199006000-00016
Guth AA, Gouge TH, Depan HJ. Blast injury to the thoracic esophagus. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991;51(5):837-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-4975(91)90147-I
Ribet M, Pruvot FR. Les ruptures barotraumatiques de l’oesophage. 4 cas. Revue de la littérature [Barotraumatic rupture of the esophagus. 4 cases. Review of the literature]. J Chir (Paris). 1986;123(3):164-8.
Chien LC, Chang HT, Chou YP. Barotraumatic oesophageal perforation with bilateral tension pneumothorax. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009;10(1):152-3. https://doi.org/10.1510/icvts.2009.212415
Novomeský F. Gastro-esophageal barotrauma in diving: Similarities with Mallory-Weiss syndrome. Soud Lek. 1999;44(2):21-4.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














