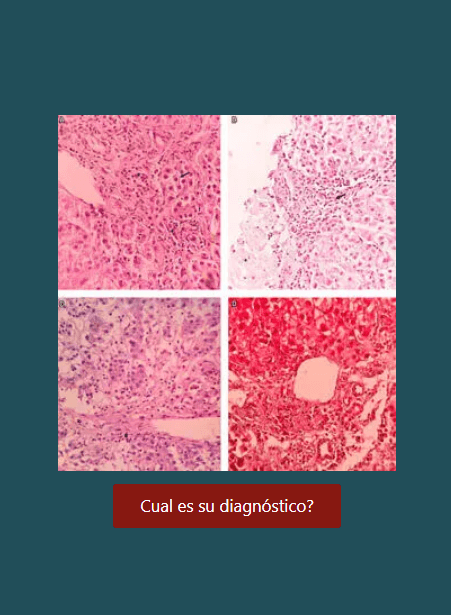
Colitis ulcerativa grave en paciente con infección por virus de inmunodeficiencia humana: reporte de caso
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.119Palavras-chave:
Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal, colitis ulcerativa, virus de inmunodeficiencia humanaResumo
Se presenta el caso de un paciente con colitis ulcerativa (CU) grave de nueva aparición y diagnóstico simultáneo de infección por virus de inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH). Dos enfermedades inmunológica y fisiopatológi- camente opuestas, que raramente se asocian. Incluso se plantea que en la infección por VIH, la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII) puede ser menos agresiva. El diagnóstico se convierte en un reto, dado el espectro de enfermedades que pueden afectar el colón en el contexto de infección por VIH. Asimismo, el tratamiento es controversial teniendo en cuenta que el uso de inmunomoduladores o biológicos bloquean otro componente del sistema inmune que podría potenciar el estado de inmunosupresión en este grupo de pacientes. La historia natural, el tratamiento y el pronóstico, continúan siendo un desafío para la evidencia actual.
Downloads
Referências
Shih D, Targan S MD. Recent advances in IBD pathogene- sis: genetics and immunobiology. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2008;10:568-75.
Viazis N, Vlachogiannakos J, Georgiou O, et al. Course of inflammatory bowel disease in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16(3):507-11.
Mehandru S, Poles MA, Tenner-Racz K, et al. Primary HIV-1 infection is associated with preferential depletion of CD4+ T lymphocytes from effector sites in the gastrointes- tinal tract. J Exp Med. 2004;200(6):761-70.
Ho TH, Cohen BL, Colombel JF, et al. Review article: The intersection of mucosal pathophysiology in HIV and inflam- matory bowel disease, and its implications for therapy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40(10):1171-86.
Mehandru S, Poles MA, Tenner-Racz K, et al. Mechanisms of gastrointestinal CD4+ T-cell depletion during acute and early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol. 2007;81:599-612.
Soria A, Rossi M, Muscatello A, et al. HIV testing: a must for patients with inflammatory bowel disease? Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(9):1727-8.
Yoshida EMMD, Chan NHLMD, Herrick RABA, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus infection, the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996;23(1):24-18.
de Oliveira Pinto LM. Garcia S, Lecoeur H, et al. Increased sensitivity of T lymphocytes to tumor necrosis factor recep- tor 1 (TNFR1)- and TNFR2-mediated apoptosis in HIV infection: relation to expression of Bcl-2 and active cas- pase-8 and caspase-3. Blood. 2002;99:1666-75.
Herbein GKK. Is HIV infection a TNF receptor signalling driven disease? Trends Immunol. 2008;29:61-7.
Shale MJ, Seow CH, Coffin CS, et al. Review article: Chronic viral infection in the anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy era in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31(1):20-34.
Cicala C, Martinelli E, McNally JP, et al. The integrin alpha- 4beta7 forms a complex with cell-surface CD4 and defines a T-cell subset that is highly susceptible to infection by HIV-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20877-82.
Chamberlain FE, Dinani N, Jagjit Singh GK, et al. Azathioprine can be safely used in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 2014;28(3):447-8.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Métricas do artigo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas abstratas | |
| Visualizações da cozinha | |
| Visualizações de PDF | |
| Visualizações em HTML | |
| Outras visualizações | |