Stents metálicos autoexpandibles para el manejo endoscópico de las fístulas esofágicas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.646Palavras-chave:
Fístulas esofágicas, Stent metálico autoexpandible, Anastomosis, Complicaciones, Cirugía de esófagoResumo
Objetivos: mostrar la eficacia y seguridad de los stents metálicos autoexpandibles para el manejo endoscópico de las fístulas esofágicas.
Materiales y métodos: se evalúo una serie de casos de manera retrospectiva entre el 2007 y el 2017, en los que se manejaron a 11 pacientes con un stent metálico autoexpandible para el manejo de fístula esofágica, en quienes se realizó el diagnóstico por clínica, endoscopia digestiva alta o estudios radiológicos en la unidad de gastroenterología del Hospital Universitario San Ignacio (HUSI) de Bogotá D. C., Colombia.
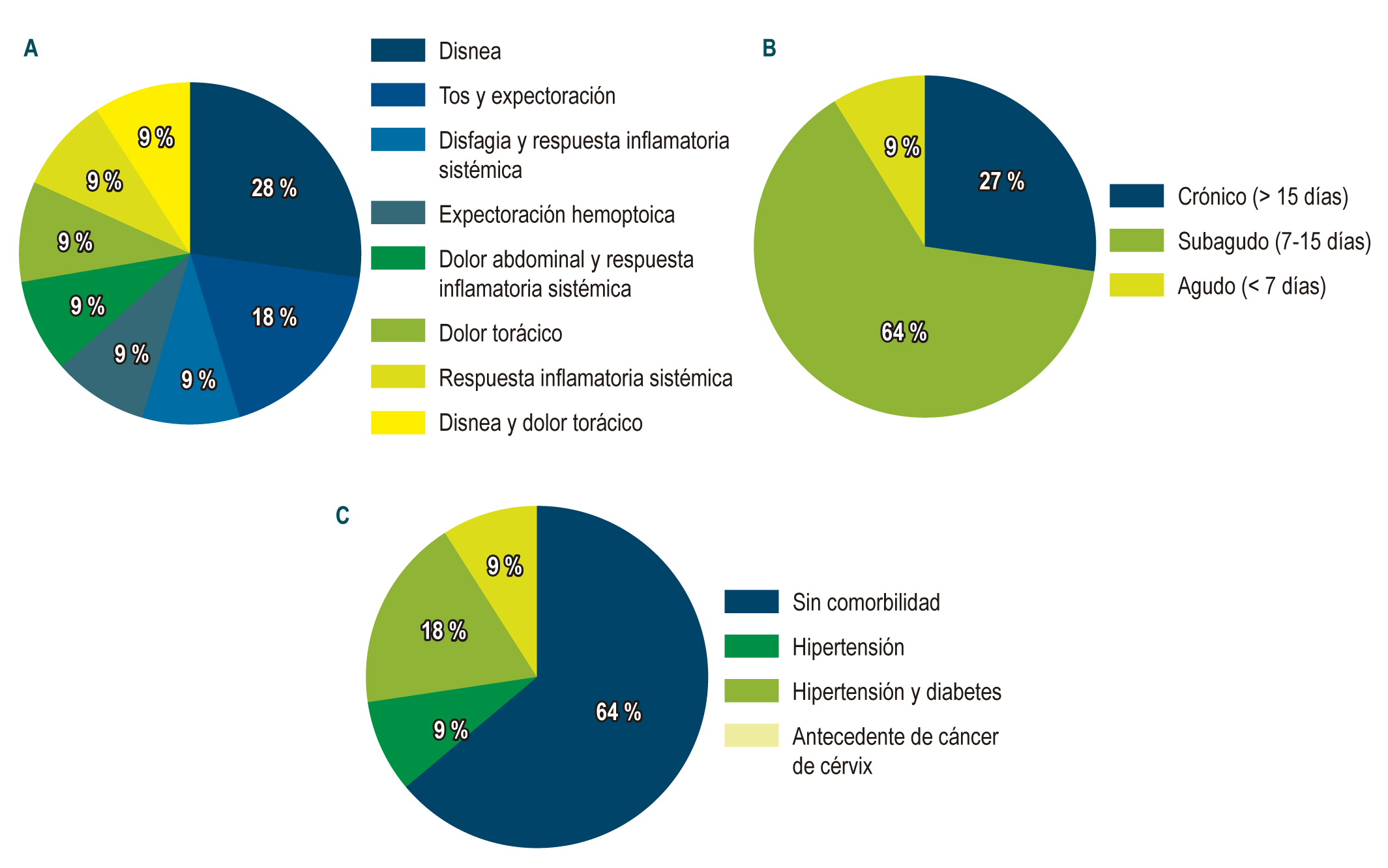
Resultados: el principal síntoma inicial fue la disnea en 27,3 % de los casos, seguido por tos en un 18,2 %. El hallazgo más frecuentemente encontrado durante el seguimiento fue el derrame pleural en el 36,4 %, se realizó el diagnóstico de fístula en el 45,5 % con esofagograma y el tipo de lesión más reportada fue la fuga en la anastomosis esofagoentérica, con un 45,5 %, seguida de la esofagopleural, con un 36,4 %; y estos pacientes fueron manejados con un stent metálico autoexpandible. En el 100 % hubo éxito técnico y la resolución del defecto se evidenció en el 72,7 % de los casos. La única complicación reportada fue el desplazamiento del stent en el 27,3 %, y en un paciente se requirió el cambio del stent en 3 oportunidades. El promedio de estancia hospitalaria fue de 41,5 días.
Conclusiones: el manejo endoscópico de las fístulas esofagogástricas con stents metálicos autoexpandibles es efectivo y seguro, con una baja tasa de complicaciones.
Downloads
Referências
Bemelman WA, Baron TH. Endoscopic Management of Transmural Defects, Including Leaks, Perforations, and Fistulae. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(7):1938-1946.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.067
Cereatti F, Grassia R, Drago A, Conti CB, Donatelli G. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal leaks and fistulae: What option do we have? World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26(29):4198-4217. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i29.4198
Falconi M, Pederzoli P. The relevance of gastrointestinal fistulae in clinical practice: a review. Gut. 2001 Dec;49 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):iv2-10. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.49.suppl_4.iv2
González-Pinto I, González EM. Optimising the treatment of upper gastrointestinal fistulae. Gut. 2001;49 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):iv22-31. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.49.suppl_4.iv21
Ge PS, Thompson CC. The Use of the Overstitch to Close Perforations and Fistulas. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2020;30(1):147-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giec.2019.08.010
Datta V, Windsor AC. Surgical management of enterocutaneous fistula. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2007;68(1):28-31. https://doi.org/10.12968/hmed.2007.68.1.22652
Kwon SH, Oh JH, Kim HJ, Park SJ, Park HC. Interventional management of gastrointestinal fistulas. Korean J Radiol. 2008;9(6):541-9. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.6.541
Schecter WP. Management of enterocutaneous fistulas. Surg Clin North Am. 2011;91(3):481-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2011.02.004
Dasari BV, Neely D, Kennedy A, Spence G, Rice P, Mackle E, Epanomeritakis E. The role of esophageal stents in the management of esophageal anastomotic leaks and benign esophageal perforations. Ann Surg. 2014;259(5):852-60. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000000564
Rodrigues-Pinto E, Repici A, Donatelli G, Macedo G, Devière J, van Hooft JE, Campos JM, Galvao Neto M, Silva M, Eisendrath P, Kumbhari V, Khashab MA. International multicenter expert survey on endoscopic treatment of upper gastrointestinal anastomotic leaks. Endosc Int Open. 2019;7(12):E1671-E1682. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1005-6632
Ross WA, Alkassab F, Lynch PM, Ayers GD, Ajani J, Lee JH, Bismar M. Evolving role of self-expanding metal stents in the treatment of malignant dysphagia and fistulas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65(1):70-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2006.04.040
Blackmon SH, Santora R, Schwarz P, Barroso A, Dunkin BJ. Utility of removable esophageal covered self-expanding metal stents for leak and fistula management. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89(3):931-6; discussion 936-7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2009.10.061
Tuebergen D, Rijcken E, Mennigen R, Hopkins AM, Senninger N, Bruewer M. Treatment of thoracic esophageal anastomotic leaks and esophageal perforations with endoluminal stents: efficacy and current limitations. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12(7):1168-76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0500-4
Doniec JM, Schniewind B, Kahlke V, Kremer B, Grimm H. Therapy of anastomotic leaks by means of covered self-expanding metallic stents after esophagogastrectomy. Endoscopy. 2003;35(8):652-8. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-41509
Roy-Choudhury SH, Nicholson AA, Wedgwood KR, Mannion RA, Sedman PC, Royston CM, Breen DJ. Symptomatic malignant gastroesophageal anastomotic leak: management with covered metallic esophageal stents. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(1):161-5. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.176.1.1760161
Siersema PD, Homs MY, Haringsma J, Tilanus HW, Kuipers EJ. Use of large-diameter metallic stents to seal traumatic nonmalignant perforations of the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58(3):356-61. ttps://doi.org/10.1067/s0016-5107(03)00008-7
Kauer WK, Stein HJ, Dittler HJ, Siewert JR. Stent implantation as a treatment option in patients with thoracic anastomotic leaks after esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. 2008;22(1):50-3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9504-5
Urschel JD. Esophagogastrostomy anastomotic leaks complicating esophagectomy: a review. Am J Surg. 1995;169(6):634-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(99)80238-4
Gelbmann CM, Ratiu NL, Rath HC, Rogler G, Lock G, Schölmerich J, Kullmann F. Use of self-expandable plastic stents for the treatment of esophageal perforations and symptomatic anastomotic leaks. Endoscopy. 2004;36(8):695-9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-825656
Johnsson E, Lundell L, Liedman B. Sealing of esophageal perforation or ruptures with expandable metallic stents: a prospective controlled study on treatment efficacy and limitations. Dis Esophagus. 2005;18(4):262-6.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2050.2005.00476.x
Raijman I. Endoscopic management of esophagorespiratory fistulas: expanding our options with expandable stents. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(4):496-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.496_b.x
Ramirez FC, Dennert B, Zierer ST, Sanowski RA. Esophageal self-expandable metallic stents--indications, practice, techniques, and complications: results of a national survey. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;45(5):360-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70144-5
Song HY, Park SI, Jung HY, Kim SB, Kim JH, Huh SJ, Kim TH, Kim YK, Park S, Yoon HK, Sung KB, Min YI. Benign and malignant esophageal strictures: treatment with a polyurethane-covered retrievable expandable metallic stent. Radiology. 1997;203(3):747-52. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.203.3.9169699
Wadhwa RP, Kozarek RA, France RE, Brandabur JJ, Gluck M, Low DE, Traverso LW, Moonka R. Use of self-expandable metallic stents in benign GI diseases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58(2):207-12. https://doi.org/10.1067/mge.2003.343
Lee SH. The role of oesophageal stenting in the non-surgical management of oesophageal strictures. Br J Radiol. 2001;74(886):891-900. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.74.886.740891
Thiruvengadam NR, Hamerski C, Nett A, Bhat Y, Shah J, Bernabe J, Kane S, Binmoeller K, Watson RR. Combination Endoscopic Therapy is Effective for Treatment of Nonbariatric Postoperative Gastroenteric Leaks. Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2021;23(2):122-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tige.2020.11.003
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Métricas do artigo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas abstratas | |
| Visualizações da cozinha | |
| Visualizações de PDF | |
| Visualizações em HTML | |
| Outras visualizações | |