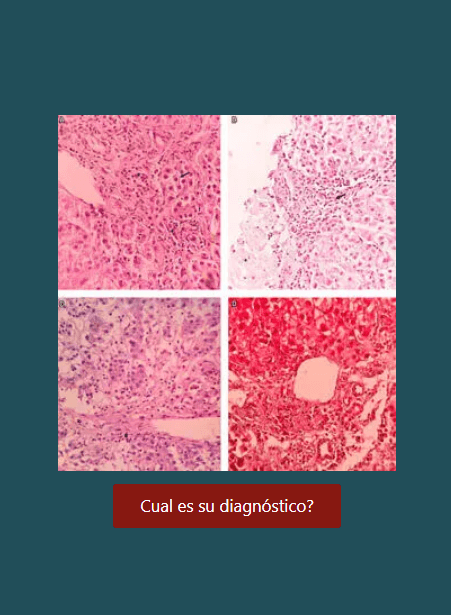
Síndrome de Budd Chiari: revisión de tema
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.97Palavras-chave:
Síndrome de Budd-Chiari, Ultrasonografía Doppler, Tomografía, Angiografía de Sustracción Digital, Trasplante de hígadoResumo
El Síndrome de Budd-Chiari (SBC) es una entidad poco usual; su incidencia se calcula de uno en cien mil. Consiste en una obstrucción completa o parcial del flujo venoso localizada en cualquier lugar desde las pe- queñas venas hepáticas hasta la porción suprahepática de la vena cava inferior. De acuerdo con su etiología puede clasificarse en: primario (cuando la obstrucción se debe a una enfermedad venosa), o secundario (cuando se atribuye a una compresión extrínseca o a la invasión por una lesión que se origina fuera de las venas como neoplasias o quistes). En la mayoría de los casos se presenta como un cuadro de inicio súbito de dolor abdominal, ascitis y hepatomegalia, pudiendo ser asintomático. El diagnóstico definitivo se establece por estudios de imagen; si bien deben solicitarse exámenes básicos de laboratorio y estudios de extensión. Las modalidades de imagen incluyen la ultrasonografía Doppler, la tomografía computarizada, la resonancia magnética y la angiografía por sustracción digital, que es considerada el patrón de oro. La primera medida terapéutica que debe emprenderse en estos pacientes es la anticoagulación con heparina de bajo peso molecular, seguida de antagonistas de vitamina K. La mayoría de los pacientes requieren un enfoque multidisciplinario y un tratamiento escalonado que incluye procedimientos radiológicos, como la aplicación de balones y stents y la inserción de shunts portosistémicos transyugulares intrahepáticos (TIPS), procedimien- tos quirúrgicos de descomprensión y, por último, trasplante hepático.
Downloads
Referências
Budd G. En: On diseases of the liver, 1era Ed. Londres, GB: John Churchill; 1845: pp. 135.
Chiari H. Ueber die selbständige Phlebitis obliterans der Hauptstämme der Venae hepaticae als Todesursache. Beitr Pathol Anat Allg Pathol. 1899;26:1-18.
Ferral H, Behrens G, Lopera J. Budd-Chiarisyndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(4):737-45.
Mac Nicholas R, Olliff S, Elias E, Tripathi D. An update on the diagnosis and management of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;6(6):731-44.
Janssen H, García J, Elias E, Mentha G, Hadengue A, Valla D. Budd–Chiari syndrome: a review by an expert panel. Journal of Hepatology. 2003;38(3):364–371.
Plessier A, Rautou PE,Valla DC. Management of hepatic vascular diseases.J Hepatol. 2012; 56 Suppl 1:S25-38. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(12)60004-X.
Aydinli M, Bayraktar Y. Budd-Chiari syndrome: etiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 21;13(19):2693-6.
Plessier A, Valla D. Budd–Chiari Syndrome. Semin Liver Dis 2008;28(3):259-269.
Valla D. The diagnosis and management of the Budd-Chiari syndrome: consensus and controversies. Hepatology. 2003;38(4):793-803.
Shrestha S, Okuda K, Uchida T, Maharjan K, Shrestha S, Joshi B, et al. Endemicity and clinical picture of liver disease due to obstruction of the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava in Nepal. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996;11(2):170–179.
Valla D. Hepatic venous outflow tract obstruction etipatho- genesis: Asia versus the West. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19:S204–S211.
De Franchis R; Baveno V Faculty. Revising consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno V consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in por- tal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2010;53(4):762-8.
Brancaccio V, Iannaccone L, Margaglione M, Guardascione MA, Amitrano L. Multiple thrombophilic factors in a patient with Budd-Chiari syndrome. Clin Lab Haematol. 2002;24(1):61-3.
DeLeve LD, Valla DC, García-Tsao G; American Association for the Study Liver Diseases. Vascular disorders of the liver. Hepatology. 2009;49(5):1729-64.
Hirshberg B, Shouval D, Fibach E, Friedman G, Ben D. Flow cytometric analysis of autonomous growth of erythroid pre- cursors in liquid culture detects occult polycythemia vera in the Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Hepatol. 2000;32:574-578.
Denninger M, Chait Y, Casadevall N, Hillaire S, Guillin M, Bezeaud A, et al. Cause ofportal or hepatic venous throm- bosis in adults: the role of multiple concurrent factors. Hepatology 2000;31:587-591.
Janssen HL et. al. Factor V Leiden mutation, prothrom-
bin gene mutation, and deficiencies in coagulation inhibitors associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome and portal vein thrombosis: results of a case-control study. 2000;96(7):2364-8.
Muradet. al. Etiology, management, and outcome of the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Ann Intern. 2009;151(3):167-75.
Valla D, Le MG, Poynard T, Zucman N, Rueff B, Benhamou JP. Risk of hepatic vein thrombosis in relation to recent use of oral contraceptives. A case-control study. Gastroenterology. 1986;90(4):807-11.
Mohanty D, Shetty S, Ghosh K, Pawar A, Abraham P. Hereditary thrombophilia as a cause of Budd-Chiari syndrome: a study from Western India. Hepatology. 2001;34(4 Pt 1):666-70.
Minnema MC, Janssen HL, Niermeijer P, de Man RA.
Budd-Chiari syndrome: combination of genetic defects and the use of oral contraceptives leading to hypercoagulability. J Hepatol. 2000; 33(3):509-12.
Shetty S, Ghosh K. Thrombophilic dimension of Budd chiari syndrome and portal venous thrombosis a concise review. Thromb Res. 2011;127(6):505-12.
P. Deltenre, M.H. Denninger, S. Hillaire, M.C. Guillin, N. Casadevall, J. Brière et al. Factor V Leiden related Budd- Chiari syndrome. Gut. 2001;48(2)264–268.
Buzas C, Sparchez Z, Cucuianu A, Manole S, Lupescu I, Acalovschi M. Budd-Chiari syndrome secondary to poly- cythemia vera. A case report. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2009;18(3):363-6.
Dayal S, Patti HP, Acharya SK. Polycythemia vera: overt to latent form in a patient with Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996;22(1):76-7.
Wanless IR, Peterson P, Das A, Boitnott JK, Moore GW, Bernier V. Hepaticvascular disease and portal hypertension in polycythemia vera and agnogenic myeloid metaplasia: a clinicopathological study of 145 patientsexamined at autopsy. Hepatology. 1990;12(5):1166-74.
Qi X, He C, Han G, Yin Z, Wu F, Zhang Q, Niu J, Wu K, Fan D. Prevalence of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in Chinese patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome or portal vein thrombosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(1):148-52.
P. Hillmen, S.M. Lewis, M. Bessler, L. Luzzatto, J.V. Dacie. Natural history of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N Engl J Med. 1995;33:1253–1258.
Yılmaz B, Köklü S, Bayraktar Y. Ulcerative colitis pre- senting with Budd-Chiari Syndrome. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(2):e74-5.
Boutachali S, Arrivé L. Budd-Chiari syndrome secondary to hepatocellular carcinoma.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2011;35(11):693-4.
Bittencourt Mde J, Dias CM, Lage TL, Barros RS, Paz OA, Vieira Wde B. Behçet disease in association with Budd- Chiari syndrome and multiple thrombosis-Case report. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88(3)448-451.
Carvalho D, Oikawa F, Matsuda NM, Yamada AT. Budd- Chiari syndrome in association with Behçet’s disease: review of the literature. Sao Paulo Med J. 2011;129(2):107-9
Afredj N, Metatla S et al. Association of Budd-Chiari syndrome and celiac disease. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2010;34(11):621-4.
Witte CL, Witte MH, Dumont AE. Lymph imbalance in the genesis and perpetuation of the ascites syndrome in hepatic cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1980;78(5 Pt 1):1059-68.
Meacham, G. C., Tillotson, F. W., Heinle, R. W., Hoyumpa, A. M., Schiff, L., Helfman, E. L., & Failing, R. M. Hepatic vein occlusion. Br Med J. 1971;4(5774):550.
Tanaka M, Wanless IR. Pathology of the liver in Budd-Chiari syndrome: portal vein thrombosis and the histogenesis of veno-centric cirrhosis, veno-portal cirrhosis, and large rege-nerative nodules. Hepatology. 1998;27(2):488-96.
De, Portmann B, Williams R. Nodular regenerative hyper- plasia of the liver and the Budd-Chiari syndrome.Case report, review of the literature and reappraisal of pathogene-sis. J Hepatol. 1991;12(1):28-35.
Darwish M, Plessier, MD; Hernández-Guerra, MD. Etiology,
Management, and Outcome of the Budd-Chiari Syndrome. EN-Vie (European Network for Vascular Disorders of the Liver). Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(3):167-75.
Cheng D, Xu H, Lu ZJ, Hua R, Qiu H, Du H, Xu X, Zhang J Clinical features and etiology of Budd-Chiari syndrome in Chinese patients: a single-center study. J Gastroenterol 2013;28(6):1061-7.
Aydinli M, Bayraktar Y. Budd-Chiari syndrome: Etiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(19):2693-2696.
Bolondi L. et. al. Diagnosis of Budd-Chiari Syndrome by pulsed Doppler ultrasound. Gastroenterology. 1991;100(5 Pt 1):1324-31.
Liao JT, Xiao Y, Huang TH, Pan RZ, Wang SC, Huang YJ. Color Doppler flow image of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007;32(1):170-3.
Boozari B, Bahr MJ, Kubicka S, Klempnauer J, Manns MP, Gebel M. Ultrasonography in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome: diagnostic signs and prognostic implications. J Hepatol. 2008;49(4):572-80.
Sakugawa H, Higashionna A, Oyakawa T, Kadena K, Kinjo F, Saito A. Ultrasound study in the diagnosis of primary Budd-Chiari syndrome (obstruction of the inferior vena cava). Gastroenterol Jpn. 1992;27(1):69-77.
Zhang R, Qin S, Zhou Y, Song Y, Sun L. Comparison of imaging characteristics between hepatic benign regenera- tive nodules and hepatocellular carcinomas associated with Budd-Chiari syndrome by contrast enhanced ultrasound. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(11):2984-9.
Patil P, Deshmukh H, Popat B, Rathod K. Spectrum of imaging in Budd Chiari syndrome. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012;56(1):75-83.
Maetani Y. et. al. Benign hepatic nodules in Budd-Chiari syn- drome: radiologic-pathologic correlation with emphasis on the central scar. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(4):869-75.
Vilgrain Vet. Al. Hepatic nodules in Budd-Chiari syndrome: imaging features.Radiology. 1999;210(2):443-50.
Lupescu IG, Dobromir C, Popa GA, Gheorghe L, Georgescu SA. Spiral computed tomography and magnetic reso- nance angiography evaluation in Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2008;17(2):223-6.
Datta DV, Vashishta S, Samanta AK, Chhuttani PN. Diagnostic value of combined transhepatic venography and inferior vena cavography in chronic Budd-Chiari syndrome. Am J Dig Dis. 1978;23(11):1031-41.
Virmani V, Khandelwal N, Kang M, Gulati M, Chawla Y. MDCT venography in the evaluation of inferior vena cava in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2009;28(1):17-23.
Lu X et. al. Study on between magnetic resonance venography and digital subtraction angiography on the inferior vena cava obstructive interface morphology of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2011;19(12):923-6.
Tanaka M, Wanless I. Pathology of the liver in Budd–Chiari syndrome: portal vein thrombosis and the histogenesis of veno-centric cirrhosis, veno-portal cirrhosis, and large rege- nerative nodules. Hepatology. 1998;27:488–496.
Ibarrola C, Castellano VM, Colina F. Focal hyperplastic hepatocellular nodules in hepatic venous outflow obstruc- tion: a clinicopathological study of four patients and 24 nodules. Histopathology. 2004;44:172-179.
Darwish S, Plessier M, Hernández M, Fabris F, Eapen C, Bahr M, et al. Etiology, management, and outcome of the Budd- Chiari syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(3):167–175.
Zimmerman M, Cameron A, Ghobrial R. Budd-Chiari syn- drome. Clin Liver Dis. 2006;10(2): 259–273.
Plessier A, Sibert A, Consigny Y, Hakime A, Zappa M, Denninger M, et al. Aiming at minimal invasiveness as a the- rapeutic strategy for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Hepatology. 2006; 44(5):1308–1316.
Menon K, Shah V, Kamath P. The Budd-Chiari syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(6):578–585.
Ki M, Chi H, Kim K, Kim B, Jang E, Jeong S. Incidence, Prevalence, and Complications of Budd-Chiari Syndrome in South Korea: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study. Liver Int. 2015; 36(7):1067-73.
Randi M, Tezza F, Scapin M, Duner E, Scarparo P, Scandellari R, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in patients with Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative disorders and unusual splanchnic or cerebral vein thrombo- sis. Acta Haematol. 2010;123(3):140–145.
Min A, Atillasoy E, Schwartz M, Thiim M, Miller C, Bodenheimer H. Reassessing the role of medical therapy in the management of hepatic vein thrombosis. Liver Transpl Surg 1997;3(4):423 –429.
Darwish S, Valla D, de Groen P, Zeitoun G, Hopmans J, Haagsma E, et al. Determinants of survival and the effect of portosystemic shunting in patients with Budd-Chiari syn- drome. Hepatology. 2004;39(2):500–508.
Rautou PE, Douarin L, Denninger M, Escolano S, Lebrec D, Moreau R, et al. Bleeding in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Hepatol. 2011;54(1):56-63.
Zaman A, Chalasani N. Bleeding caused by portal hyperten- sion. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2005;34(4):623–642.
Greenwood L, Yrizarry J, Hallett J, Scoville G. Urokinase treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983;141(5):1057–1059.
Kuo G, Brodsky R, Kim H. Catheter-directed thrombolysis and thrombectomy for the Budd-Chiari syndrome in paro- xysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in three patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;17(2):383–387.
Pawlak J, Palester M, Michałowicz B, Elwertowski M, Małkowski P, Szczerbień J. Thrombolytic treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome with portal venous thrombosis. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 1993;89(2):171–177.
Sharma S, Texeira A, Texeira P, Elias E, Wilde J, Olliff S. Pharmacological thrombolysis in Budd Chiari syndrome: a single centre experience and review of the literature. J Hepatol. 2004; 40(1):172–180.
EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites,
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2010;53(3):397–417.
Wang Z, Zhang F, Yi M, Qiang L. Evolution of manage- ment for Budd-Chiari syndrome: a team’s view from 2564 patients. ANZ J Surg 2005;75(1-2):55–63.
Eapen C, Velissaris D, Heydtmann M, Gunson B, Olliff S, Elias E. Favourable medium term outcome following hepatic vein recanalisation and/or transjugular intrahepa- tic portosystemic shunt for Budd Chiari syndrome. Gut. 2006;55(6):878–884.
Plessier A. Budd Chiari syndrome. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006;30:1162–1169.
Yang X, Cheng T, Chen C. Successful treatment by percuta- neous balloon angioplasty of Budd-Chiari syndrome caused by membranous obstruction of inferior vena cava: 8-year follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996;28(7):1720–1724.
Li T, Zhai S, Pang Z, Ma X, Cao H, Bai W, et al. Feasibility and midterm outcomes of percutaneous transhepatic balloon angioplasty for symptomatic Budd-Chiari syndrome secondary to hepatic venous obstruction. J Vasc
Surg. 2009;50(5):1079–1084.
Fisher N, McCafferty I, Dolapci M, Wali M, Buckels J, Olliff S, et al. Managing Budd-Chiari syndrome: a retrospective review of percutaneous hepatic vein angioplasty and surgi- cal shunting. Gut. 1999:44(4):568–574.
Witte A, Kool L, Veenendaal R, Lamers C, van Hoek B. Hepatic vein stenting for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(3):498–501.
Zhang C, Fu L, Xu L, Zhang G, Jia T, Liu JY, et al. Long-term effect of stent placement in 115 patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9(11):2587- 2591.
Ding P, Han X, Wu G, Li Y, Shui S, Wang Y. Outcome of a retrieval stent filter and 30 mm balloon dilator for patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome and chronic inferior vena cava thrombosis: a prospective pilot study. Clin Radiol.
;65(8):629–635.
Wang Y, Ding P, Li Y, Han X, Wu G. Comparative study of
predilation with stent filter for Budd-Chiari syndrome with old IVC thrombosis: a nonrandomized prospective trial. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(6):1158–1164.
García J, Heydtmann M, Raffa S, Plessier A, Murad S, Fabris F, et al. TIPS for Budd-Chiari syndrome: long-term results and prognostics factors in 124 patients. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135(3):808–815.
Casado M, Bosch J, García J, Bru C, Bañares R, Bandi J, et al. Clinical events after transjugular intrahepatic por- tosystemic shunt: correlation with hemodynamic findings. Gastroenterology. 1998;114(6):1296–1303.
Watanabe H, Shinzawa H, Saito T, Ishibashi M, Shirahata N, Miyano S, et al. Successful emergency treatment with a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for life-threatening Budd-Chiari syndrome with portal thrombotic obstruction. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47(33): 839–841.
Shrestha R, Durham J, Wachs M, Bilir B, Kam I, Trouillot T, et al. Use of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt as a bridge to transplantation in fulminant hepatic failure due to Budd-Chiari syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997;92(12):2304–2306.
Neumann A, Andersen S, Nielsen D, Holland P, Vilstrup H, Grønbæk H. Treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome with a focus on transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. World J Hepatol. 2013;5(1):38-42.
Attwell A, Ludkowski M, Nash R, Kugelmas M. Treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome in a liver transplant unit, the role of transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt and liver trans- plantation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20(8):867–873.
Langnas A, Marujo W, Stratta R, Donovan J, Sorrell M, Rikkers L, et al. Influence of a prior porta-systemic shunt on outcome after liver transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992;87(6):714–718.
Bismuth H, Sherlock D. Portasystemic shunting versus liver transplantation for the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Ann Surg. 1991;214(5):581–589.
Xu P, Ma X, Ye X, Feng L, Dang X, Zhao Y, et al. Surgical treatment of 1360 cases of Budd-Chiari syndrome: 20-year experience. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004;3(3):391–394
Orloff M, Johansen K. Treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome by side-to-side portacaval shunt: experimental and clinical results. Ann Surg. 1978;188(4):494-512.
Orloff M, Girard B. Long term results of treatment of Budd- Chiari syndrome by side to side portacaval shunt. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989;168(1):33–41.
Cameron J, Herlong H, Sanfey H, Boitnott J, Kaufman S, Gott V, et al. The Budd-Chiari syndrome. Treatment by mesenteric-systemic venous shunts. Ann Surg. 1983;198(3):335–346. Chen H, Zhang F, Ye Y, Cheng Y, Chen Y. Long-term follow- up study and comparison of meso-atrial shunts and meso- cavo-atrial shunts for treatment of combined Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Surg Res. 2011;168(1):162–166.
Orloff M, Isenberg J, Wheeler H, Daily P, Girard B. Budd-Chiari syndrome revisited: 38 years’ experience with surgical portal decompression. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16(2):286–300.
Mancuso A. Budd-chiari syndrome management: Timing of treatment is an open issue. Hepatology. 2014;59(3):1213.
Rautou P, Moucari R, Cazals D, Escolano S, Denié C, Douarin L, et al. Levels and initial course of serum ala- nine aminotransferase can predict outcome of patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(11):1230–1235.
Putnam C, Porter K, Weil R III, Weil R, Reid H, Starzl T. Liver transplantation of Budd Chiari syndrome. JAMA. 1976;236(10):1142–1143.
Campbell D, Rolles K, Jamieson N, O’Grady J, Wight D, Williams R, et al. Hepatic transplantation with perioperative and long term anticoagulation as treatment for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988;166(6):511–518.
Knoop M, Lemmens H, Bechstein W, Blumhardt G, Schattenfroh N, Keck H, et al. Treatment of the Budd-Chiari syndrome with orthotopic liver transplantation and long- term anticoagulation. Clin Transplant. 1994;8(1):67–72.
Mentha G, Giostra E, Majno PE, Bechstein W, Neuhaus P, O’Grady J, et al. Liver transplantation for Budd-Chiari syn- drome: A European study on 248 patients from 51 centres. J Hepatol. 2006;44(3):520–528.
Ringe B, Lang H, Oldhafer K, Gebel M, Flemming P, Georgii A, et al. Which is the best surgery for Budd-Chiari syndrome: venous decompression or liver transplantation? A single-center experience with 50 patients. Hepatology. 1995;21(5):1337–1344.
Shaked A, Goldstein R, Klintmalm G, Drazan K, Husberg B, Busuttil R .
Portosystemic shunt versus orthotopic liver transplantation for the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1992; 174(6):453–459.
Ulrich F, Pratschke J, Neumann U, Pascher A, Puhl G,
Fellmer P, et al. Eighteen years of liver transplantation expe- rience in patients with advanced Budd-Chiari syndrome. Liver Transpl. 2008;14(2):144–150.
Segev D, Nguyen G, Locke J, Simpkins C, Montgomery R, Maley W, et al Twenty years of liver transplantation for Budd-Chiari syndrome: a national registry analysis. Liver Transpl 2007; 13(9):1285–1294.
Srinivasan P, Rela M, Prachalias A, Muiesan P, Portmann B, Mufti G, et al. Liver transplantation for Budd-Chiari syn- drome. Transplantation. 2002;73(6):973–977.
Klein A, Molmenti E. Surgical treatment of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Liver Transpl. 2003;9 (9):891–896.
Jamieson N, Williams R, Calne R. Liver transplanta- tion for Budd-Chiari syndrome, 1976–1990. Ann Chir. 1991;45(4):362–365.
Valla D. Primary Budd-Chiari syndrome. J Hepatol. 2009;50(1):195-203.
Langlet P, Escolano S, Valla D, Coste D, Denie C, Mallet A, et al. Clinicopathological forms and prognostic index in Budd- Chiari syndrome. Journal of Hepatology. 2003;39(4)496–501.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.

| Métricas do artigo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas abstratas | |
| Visualizações da cozinha | |
| Visualizações de PDF | |
| Visualizações em HTML | |
| Outras visualizações | |