Esophagogastric Junction Contractile Integral (EGJ-CI) in Various Phenotypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1066Keywords:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Esophagogastric junction, Lower esophageal sphincterAbstract
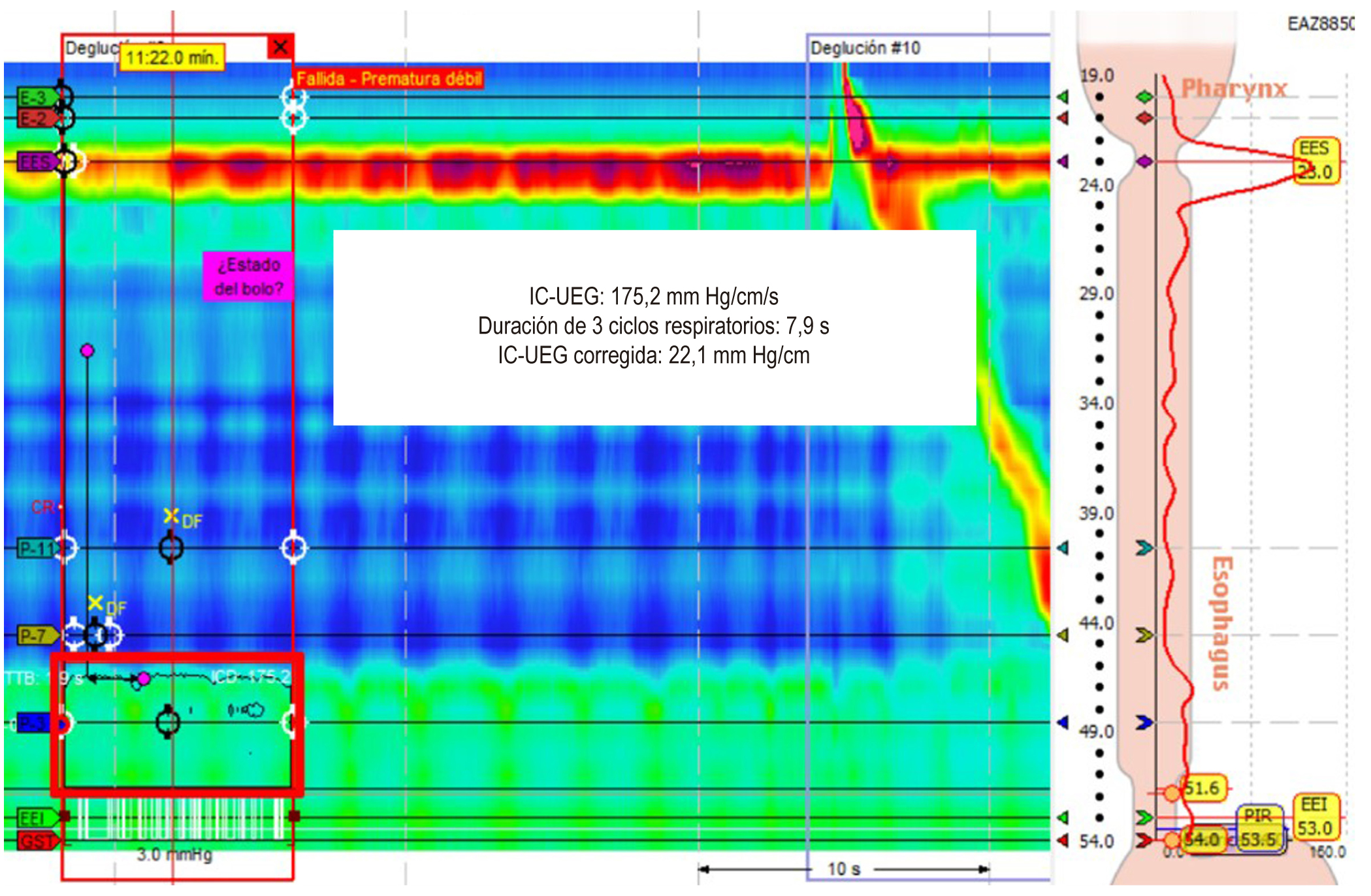
Introduction: Two parameters of high-resolution esophageal manometry are used to observe the function of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ): the anatomical morphology of the EGJ and contractile vigor, which is evaluated with the esophagogastric junction contractile integral (EGJ-CI). To date, how these parameters behave in different gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) phenotypes has not been evaluated.
Materials and methods: An analytical observational study evaluated patients with GERD confirmed by pH-impedance testing and endoscopy undergoing high-resolution esophageal manometry. The anatomical morphology of the EGJ and EGJ-CI was assessed and compared between reflux phenotypes: acid, non-acid, erosive, and non-erosive.
Results: 72 patients were included (63% women, mean age: 54.9 years), 81.9% with acid reflux and 25% with erosive esophagitis. In the latter, a decrease in EGJ-CI (median: 15.1 vs. 23, p = 0.04) and a more significant proportion of patients with type IIIa and IIIb EGJ (83.3% vs 37.1%, p < 0.01) were found. No significant differences existed in the manometric parameters of patients with and without acid and non-acid reflux.
Conclusion: In our population, EGJ-CI significantly decreased in patients with erosive GERD, suggesting that it could be used to predict this condition in patients with GERD. This finding is also related to a higher proportion of type III EGJ and lower pressure at end-inspiration of the lower esophageal sphincter in this reflux type.
Downloads
References
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R, Bianchi LK, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(8):1900-20; quiz 1943. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x
Prakash Gyawali C, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout AJPM, et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut. 2018;67(7):1351-1362. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722
Prakash Gyawali C, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout AJPM, et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut. 2018;67(7):1351-1362. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722
Hani A, Bernal W, Leguízamo AM, Zuluaga C, Vargas R, Vergara H, et al. Cómo realizar e interpretar una manometría esofágica de alta resolución usando la clasificación de Chicago 3.0. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2017;32(4):369-78. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.181
Kahrilas PJ, Mittal RK, Bor S, Kohn GP, Lenglinger J, Mittal SK, et al. Chicago Classification update (v4.0): Technical review of high-resolution manometry metrics for EGJ barrier function. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33(10):e14113. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14113
Nicodème F, Pipa-Muniz M, Khanna K, Kahrilas PJ, Pandolfino JE. Quantifying esophagogastric junction contractility with a novel HRM topographic metric, the EGJ-Contractile Integral: Normative values and preliminary evaluation in PPI non-responders. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014;26(3):353-60. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12267
Katzka DA, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Phenotypes of gastroesophageal reflux disease: Where Rome, Lyon, and Montreal meet. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;18(4):767-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.015
Costa VA, Pinto Saavedra OM, Hani Amador AC, Leguízamo Naranjo AM, Ardila Hani AF. Actualización en la interpretación de la medición del pH e impedanciometría. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2021;36(1):73-80. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.608
Carlson DA, Gyawali CP, Khan A, Yadlapati R, Chen J, Chokshi RV, et al. Classifying esophageal motility by FLIP panometry: A study of 722 subjects with manometry. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(12):2357-2366. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001532
Yadlapati R, Kahrilas PJ, Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ, Prakash Gyawali C, Roman S, et al. Esophageal motility disorders on high‐resolution manometry: Chicago classification version 4.0 ©. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33(1):e14058. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14058.
Páramo-Hernández DB, Albis R, Galiano MT, de Molano B, Rincón R, Pineda-Ovalle LF, et al. Prevalencia de síntomas del reflujo gastroesofágico y factores asociados: una encuesta poblacional en las principales ciudades de Colombia. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2016;31(4):337-46. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.108
Huerta-Iga F, Bielsa-Fernández MV, Remes-Troche JM, Valdovinos-Díaz MA, Tamayo-de la Cuesta JL, en representación del Grupo para el estudio de la ERGE 2015. Diagnóstico y tratamiento de la enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico: recomendaciones de la Asociación Mexicana de Gastroenterología. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2016;81(4):208-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2016.04.003
Gor P, Li Y, Munigala S, Patel A, Bolkhir A, Gyawali CP. Interrogation of esophagogastric junction barrier function using the esophagogastric junction contractile integral: an observational cohort study: EGJ barrier function on HRM. Dis Esophagus. 2016;29(7):820-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/dote.12389
Ham H, Cho YK, Lee HH, Yoon SB, Lim CH, Kim JS, et al. Esophagogastric junction contractile integral and morphology: Two high-resolution manometry metrics of the anti-reflux barrier. J Gastroenterol Hepatol (Australia). 2017;32(8):1443-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13720
Wang D, Patel A, Mello M, Shriver A, Gyawali CP. Esophagogastric junction contractile integral (EGJ-CI) quantifies changes in EGJ barrier function with surgical intervention. Neurogastroenterology and Motility. 2016;28(5):639-46. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12757
Rogers BD, Rengarajan A, Abrahao L, Bhatia S, Bor S, Carlson DA, et al. Esophagogastric junction morphology and contractile integral on high-resolution manometry in asymptomatic healthy volunteers: An international multicenter study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33(6):e14009. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14009
Jasper D, Freitas-Queiroz N, Hollenstein M, Misselwitz B, Layer P, Navarro-Rodriguez T, et al. Prolonged measurement improves the assessment of the barrier function of the esophago-gastric junction by high-resolution manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017;29(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12925
Tolone S, de Bortoli N, Marabotto E, de Cassan C, Bodini G, Roman S, et al. Esophagogastric junction contractility for clinical assessment in patients with GERD: A real added value? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27(10):1423-31. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12638
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














