Characterization of esophageal motility disorders in refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease patients with esophageal symptoms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.678Keywords:
Refractory gastroesophageal reflux, High-resolution manometry, Esophageal motilityAbstract
Introduction: Refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can lead to potential complications such as persistent esophagitis, esophageal stricture, Schatzki ring, and Barrett's esophagus. This study describes motility in patients with refractory GERD, and its association with esophageal symptoms.
Materials and methods: An analytical observational study was carried out in a retrospective cohort of patients diagnosed with refractory GERD and esophageal symptoms who underwent high-resolution esophageal manometry and impedance testing. Clinical characteristics, demographics, and the association between motility disorders and esophageal symptoms are described.
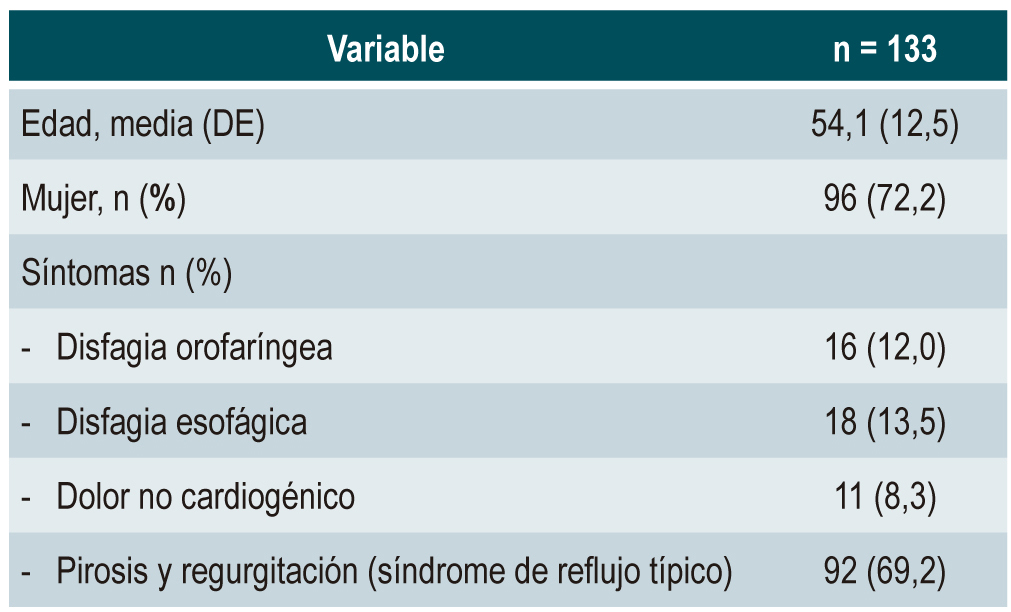
Results: 133 patients were included (mean age 54.1 ± 12.5 years). Heartburn and regurgitation (69.2%), and esophageal dysphagia (13.5%) were the most common symptoms. Normal motility (75.2%), complete bolus clearance (75.2%), and ineffective esophageal motility (IEM) (18%) were the most frequent manometric findings. Type II and IIIb gastroesophageal junction were observed in 35.3% and 33.8% of the cases, respectively. Esophageal aperistalsis (3.8%) and Jackhammer esophagus (0.8%) were rare findings. Incomplete bolus clearance was associated with esophageal dysphagia (p=0.038) and IEM (p=0.008). No esophageal symptoms were significantly related to motility disorders.
Conclusions: The results of the present study suggest that motility disorders are rare in patients with refractory GERD. They also suggest that esophageal motility disorders are not associated with the presence of esophageal symptoms and, therefore, the type of symptom experienced does not allow predicting the existence of such disorders.
Downloads
References
Rubenstein JH, Chen JW. Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2014;43(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2013.11.006
Páramo DB, Albis R, Galiano MT, Mendoza de Molano B, Rincón R, Pineda Ovalle LF, et al. Prevalencia de síntomas del reflujo gastroesofágico y factores asociados: una encuesta poblacional en las principales ciudades de Colombia. Revista Colombiana de Gastroenterología. 2016;31(4):337-46. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.108
Eusebi LH, Ratnakumaran R, Yuan Y, Solaymani-Dodaran M, Bazzoli F, Ford AC. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: a meta-analysis. Gut. 2018;67(3):430-440. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313589
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R; Global Consensus Group. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(8):1900-20; quiz 1943. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x
Yadlapati R, DeLay K. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Med Clin North Am. 2019;103(1):15-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2018.08.002
Subramanian CR, Triadafilopoulos G. Refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2015;3(1):41-53. https://doi.org/10.1093/gastro/gou061
Lin S, Li H, Fang X. Esophageal Motor Dysfunctions in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Therapeutic Perspectives. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;25(4):499-507. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm19081
Patel A, Posner S, Gyawali CP. Esophageal High-Resolution Manometry in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. JAMA. 2018;320(12):1279-1280. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.8694
Mello M, Gyawali CP. Esophageal manometry in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2014;43(1):69-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2013.11.005
Abdallah J, George N, Yamasaki T, Ganocy S, Fass R. Most Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Who Failed Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy Also Have Functional Esophageal Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(6):1073-1080.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.06.018
Stoikes N, Drapekin J, Kushnir V, Shaker A, Brunt LM, Gyawali CP. The value of multiple rapid swallows during preoperative esophageal manometry before laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc. 2012;26(12):3401-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2350-0
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, et al. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27(2):160-74. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12477
Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Mar;108(3):308-28; quiz 329. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.444
Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout AJPM, Vaezi M, Sifrim D, Fox MR, Vela MF, Tutuian R, Tack J, Bredenoord AJ, Pandolfino J, Roman S. Modern diagnosis of GERD: the Lyon Consensus. Gut. 2018;67(7):1351-1362. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314722
Armstrong D, Marshall JK, Chiba N, Enns R, Fallone CA, Fass R, et al. Canadian Consensus Conference on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease in adults - update 2004. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19(1):15-35. https://doi.org/10.1155/2005/836030
Patcharatrakul T, Gonlachanvit S. Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms in typical and atypical GERD: roles of gastroesophageal acid refluxes and esophageal motility. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(2):284-90. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12347
Abdel Jalil AA, Castell DO. Ineffective Esophageal Motility (IEM): the Old-New Frontier in Esophagology. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2016;18(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-015-0472-y
Roman S, Kahrilas PJ. Management of spastic disorders of the esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013;42(1):27-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2012.11.002
Roman S, Pandolfino JE, Chen J, Boris L, Luger D, Kahrilas PJ. Phenotypes and clinical context of hypercontractility in high-resolution esophageal pressure topography (EPT). Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(1):37-45. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2011.313
Roman S, Damon H, Pellissier PE, Mion F. Does body position modify the results of oesophageal high resolution manometry? Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22(3):271-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01416.x
Roman S, Lin Z, Kwiatek MA, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Weak peristalsis in esophageal pressure topography: classification and association with Dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106(2):349-56. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2010.384
Bulsiewicz WJ, Kahrilas PJ, Kwiatek MA, Ghosh SK, Meek A, Pandolfino JE. Esophageal pressure topography criteria indicative of incomplete bolus clearance: a study using high-resolution impedance manometry. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(11):2721-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2009.467
Bogte A, Bredenoord AJ, Oors J, Siersema PD, Smout AJ. Relationship between esophageal contraction patterns and clearance of swallowed liquid and solid boluses in healthy controls and patients with dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24(8):e364-72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01949.x
Pu L, Chavalitdhamrong D, Summerlee RJ, Zhang Q. Effects of Posture and Swallow Volume on Esophageal Motility Morphology and Probability of Bolus Clearance: A Study Using High-Resolution Impedance Manometry. Gastroenterol Nurs. 2020;43(6):440-447. https://doi.org/10.1097/SGA.0000000000000356
Zizer E, Seufferlein T, Hänle MM. Impaired bolus clearance in combined high-resolution esophageal manometry and impedance measurement helps to differentiate between esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction and achalasia. Z Gastroenterol. 2017;55(2):129-135. English. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-121267
Jain A, Baker JR, Chen JW. In ineffective esophageal motility, failed swallows are more functionally relevant than weak swallows. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30(6):e13297. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13297
Zerbib F, Marin I, Cisternas D, Abrahao L Jr, Hani A, Leguizamo AM, et al. Ineffective esophageal motility and bolus clearance. A study with combined high-resolution manometry and impedance in asymptomatic controls and patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;32(9):e13876. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13876
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














