Histopathological finding of Strongyloides stercoralis in a patient with Crohn’s disease: Case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.501Keywords:
Nematode infections, Strongyloides stercolaris;, Immunocompromised host, Hematemesis, Crohn’s DiseaseAbstract
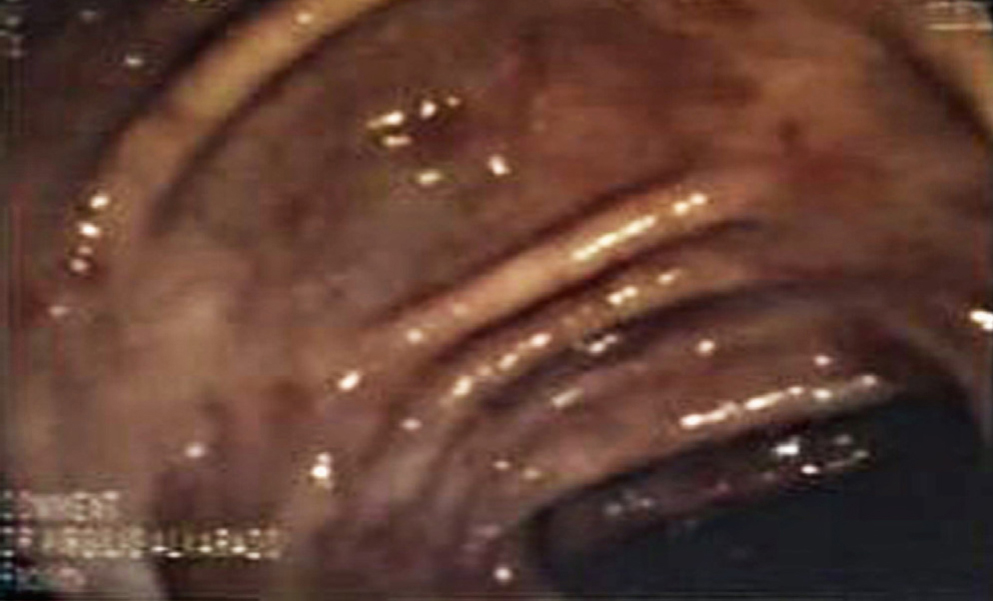
Clinical case: The following is a rare clinical case in an immunocompromised patient with histopathological findings of parasitic infestation. The patient is a middle-aged male who lives in a subtropical area and has a diagnosis of Crohn’s disease treated with corticosteroids and immunomodulators. The patient presented with abdominal pain and chronic anemia for 1 year, with negative laboratory tests for parasites and normal acute phase reactants. Gastroscopy and colonoscopy were performed before the consultation (6 months) without relevant findings. Due to the persistence of the symptoms, endoscopic studies were repeated, finding subepithelial bleeding with histopathological results of Strongyloides stercoralis.
Conclusion: In the context of an immunocompromised patient living in an endemic area and with a torpid evolution, a differential diagnosis should be made always suspecting a parasitic infestation. Although endoscopy is not necessary to diagnose strongyloidiasis, its use may be convenient.
Downloads
References
Schär F, Trostdorf U, Giardina F, Khieu V, Muth S, Marti H, et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: Global Distribution and Risk Factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(7):e2288. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002288
Newberry AM, Williams DN, Stauffer WM, Boulware DR, Hendel-Paterson BR, Walker PF. Strongyloides hyperinfection presenting as acute respiratory failure and gram-negative sepsis. Chest. 2005;128(5):3681-4. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.128.5.3681
Arévalo Suarez F, Cerrillo Sánchez G. Strongyloides stercoralis: Hallazgos Histopatológicos en Mucosa Duodenal 1999-2005. Rev Gastroenterol Perú. 2006;26(1):44-8.
Gorman SR, Craven DE. Images in clinical medicine. Strongyloides stercoralis hyperinfection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(11):e12. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMicm066791
Upadhyay D, Corbridge T, Jain M, Shah R. Pulmonary hyperinfection syndrome with Strongyloides stercoralis. Am J Med. 2001;111(2):167-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(01)00708-2
Woodring JH, Halfhill H 2nd, Reed JC. Pulmonary strongyloidiasis: clinical and imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994;162(3):537-42. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.162.3.8109492
Kim JH, Kim DS, Yoon YK, Sohn JW, Kim MJ. Donor-Derived Strongyloidiasis Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Review and Pooled Analysis. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(7):2442-2449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.11.045
Fardet L, Généreau T, Cabane J, Kettaneh A. Severe strongyloidiasis in corticosteroid-treated patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006;12(10):945-7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01443.x
Concha R, Harrington W Jr, Rogers AI. Intestinal strongyloidiasis: recognition, management, and determinants of outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39(3):203-11. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcg.0000152779.68900.33
Robinson RD, Lindo JF, Neva FA, Gam AA, Vogel P, Terry SI, et al. Immunoepidemiologic studies of Strongyloides stercoralis and human T lymphotropic virus type I infections in Jamaica. J Infect Dis. 1994;169(3):692-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/169.3.692
Scowden EB, Schaffner W, Stone WJ. Overwhelming strongyloidiasis: an unappreciated opportunistic infection. Medicine (Baltimore). 1978;57(6):527-44.
Strazzella WD, Safirstein BH. Asthma due to parasitic infestation. N J Med. 1989;86(12):947-9.
Woodring JH, Halfhill H 2nd, Berger R, Reed JC, Moser N. Clinical and imaging features of pulmonary strongyloidiasis. South Med J. 1996;89(1):10-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-199601000-00002
Lessnau KD, Can S, Talavera W. Disseminated Strongyloides stercoralis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Treatment failure and a review of the literature. Chest. 1993;104(1):119-22. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.104.1.119
Sharifdini M, Mirhendi H, Ashrafi K, Hosseini M, Mohebali M, Khodadadi H, et al. Comparison of Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction with Parasitological Methods for Detection of Strongyloides stercoralis in Human Fecal Samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93(6):1285-91. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.15-0309
Sreenivas DV, Kumar A, Kumar YR, Bharavi C, Sundaram C, Gayathri K. Intestinal strongyloidiasis--a rare opportunistic infection. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1997;16(3):105-6.
Thompson BF, Fry LC, Wells CD, Olmos M, Lee DH, Lazenby AJ, et al. The spectrum of GI strongyloidiasis: an endoscopic-pathologic study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59(7):906-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(04)00337-2
Drugs for Parasitic Infections. Treatment Guidelines from The Medical Letter. 2013;11(Suppl):e1-e31.
Henriquez-Camacho C, Gotuzzo E, Echevarria J, White AC Jr, Terashima A, Samalvides F, et al. Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;2016(1):CD007745. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007745.pub3
Zaha O, Hirata T, Kinjo F, Saito A, Fukuhara H. Efficacy of ivermectin for chronic strongyloidiasis: two single doses given 2 weeks apart. J Infect Chemother. 2002;8(1):94-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s101560200013
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














