Crohn’s Disease in a Patient with Tuberculosis: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.969Keywords:
Crohn's disease, tuberculosis, differential diagnosisAbstract
Introduction: Crohn’s disease (CD) is unusual in Colombia. Tuberculosis (TB) occurs more frequently, but intestinal involvement is rare. Differentiating these two entities and treating the cases in which they coexist is a challenge.
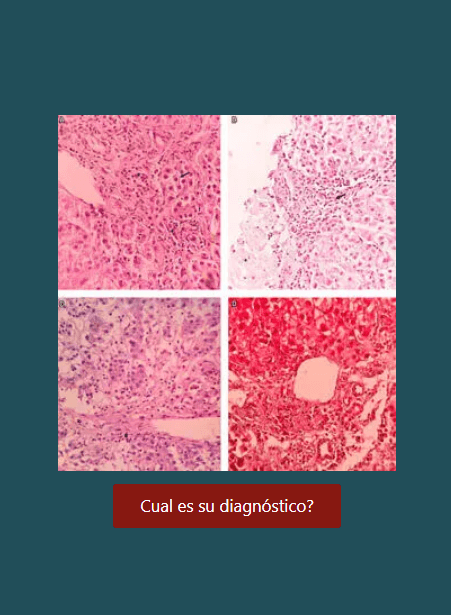
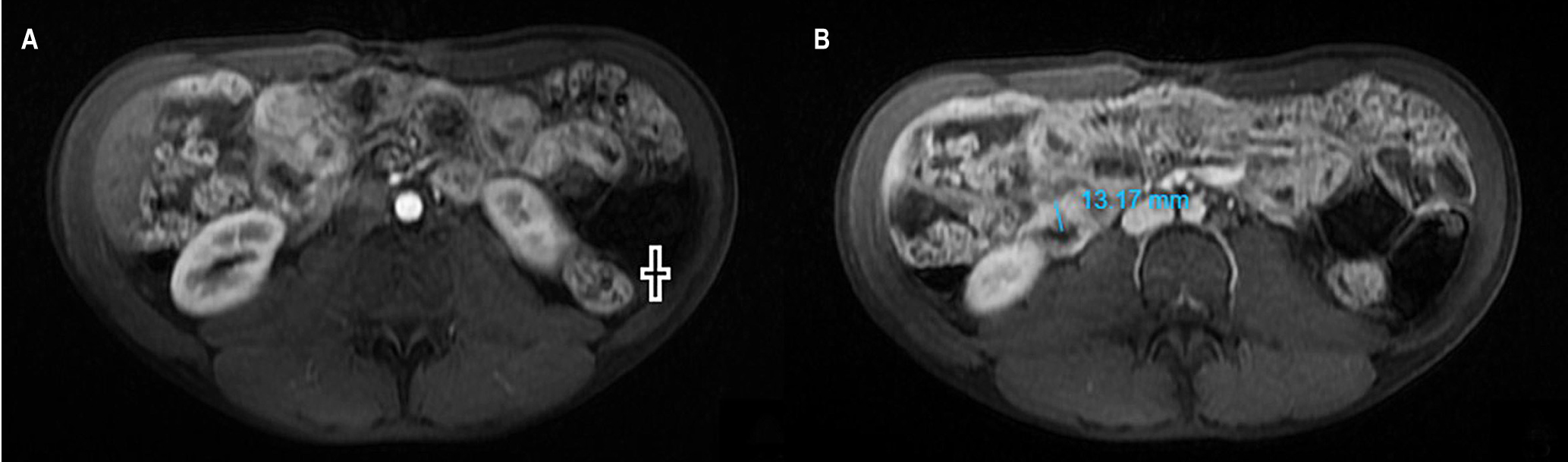
Clinical case: A 28-year-old man with three months of constitutional, respiratory, and GI symptoms was initially diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis, and all the clinical manifestations were attributed to this entity. Given the absence of improvement with treatment and the sum of radiological, endoscopic, and pathological findings, CD was confirmed. Treatment was complex due to the coexistence of the two entities, although he finally went into remission with the use of biologicals.
Discussion: Diagnosing CD requires the sum of clinical and paraclinical findings. A therapeutic test may be necessary to differentiate it from intestinal TB. The treatment of CD in a patient with TB has some limitations; steroids are not contraindicated, and biologicals must be initiated cautiously.
Conclusions: Differentiating CD from intestinal TB is a diagnostic challenge. Therapeutic management when these two entities coexist requires an interdisciplinary approach.
Downloads
References
Juliao F, Damas OM, Arrubla M, Calixto OJ, Camargo JL, Cruz L, et al. The Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Colombia is Increasing: Report on the National Prevalence of IBD and Description of IBD Phenotype. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(6):S-405-S-. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(19)37865-5
Cruz Martínez OA. Informe de evento Tuberculosis año 2021. Programa nacional de prevención y control de la tuberculosis [Internet]. Minsalud; 2021 [actualizado noviembre 2021; citado 25 de junio de 2022]. Disponible en: https://www.minsalud.gov.co/sites/rid/Lists/BibliotecaDigital/RIDE/VS/PP/ET/comportamiento-tuberculosis-2020.pdf
Raviglione MC, Gori A. Tuberculosis. En: Loscalzo J, Fauci A, Kasper D, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson JL (editores). Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine 21.a edición. Nueva York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2022. p. 1357-1381.
Eraksoy H. Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Tuberculosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.2021;50(2):341-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2021.02.004
Oñate-Ocaña LF, Pérez-Díaz L. Intestinal Tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(13):e30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMicm2114345
Bonovas S, Fiorino G, Allocca M, Lytras T, Nikolopoulos GK, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. Biologic Therapies and Risk of Infection and Malignancy in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(10):1385-97.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.04.039
Johnston RD, Logan RF. What is the peak age for onset of IBD? Inflammatory bowel diseases. 2008;14 Suppl 2:S4-5. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.20545
Juliao-Baños F, Puentes F, López R, Saffon MA, Reyes G, Parra V, et al. Characterization of inflammatory bowel disease in Colombia: Results of a national register. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (English). 2021;86(2):153-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2020.05.005
Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, management. 11.a edición. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020.
Kedia S, Das P, Madhusudhan KS, Dattagupta S, Sharma R, Sahni P, et al. Differentiating Crohn’s disease from intestinal tuberculosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(4):418-32. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i4.418
Waugh N, Cummins E, Royle P, Kandala N, Shyangdan D, Arasaradnam R, et al. Faecal calprotectin testing for differentiating amongst inflammatory and non-inflammatory bowel diseases: systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17(55):xv-xix, 1-211. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta17550
Lewis JD. The utility of biomarkers in the diagnosis and therapy of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(6):1817-26.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.058
Juliao-Baños F, Ovalle LFP, Regino WO, de Sánchez MTG, Duperly RG, Torres M. Guía de práctica clínica para el tratamiento de la enfermedad de Crohn en población adulta. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2020;35(Supl 2):63-200. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.637
Youssef J, Novosad SA, Winthrop KL. Infection Risk and Safety of Corticosteroid Use. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2016;42(1):157-76, ix-x. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2015.08.004
Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, Hendy PA, Smith PJ, Limdi JK, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 2019;68(Suppl 3):s1-s106. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318484
Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Hanauer S, Colombel JF, Sands BE, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. New Eng J Med. 2013;369(8):711-21. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1215739
Colombel JF, Sands BE, Rutgeerts P, Sandborn W, Danese S, D’Haens G, et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2017;66(5):839-51. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311079
Singh S, Fumery M, Sandborn WJ, Murad MH. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: first- and second-line biologic therapies for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48(4):394-409. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14852
Dobler CC. Biologic Agents and Tuberculosis. Microbiol Spectr. 2016;4(6). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.TNMI7-0026-2016
Matsumoto T, Tanaka T, Kawase I. Infliximab for rheumatoid arthritis in a patient with tuberculosis. New Eng J Med. 2006;355(7):740-1. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc053468
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |