Estrés, depresión, ansiedad y el hábito alimentario en personas con síndrome de intestino irritable
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.899Palabras clave:
Síndrome de Intestino Irritable, eje cerebro-intestino, microbiota, hábito alimentario, estrés, depresión, ansiedadResumen
El síndrome de intestino irritable (SII) es un trastorno caracterizado por cambios en el hábito intestinal y afecta al 30% de la población mundial. Aunque se ha encontrado una conexión entre el eje cerebro-microbiota intestinal, el desarrollo del SII y su asociación con la prevalencia de trastornos mentales, las posibles implicaciones que tienen en el hábito alimentario de las personas no son claras. Este artículo tuvo como objetivo explorar la relación entre el estrés, depresión, ansiedad, trastornos mentales y hábitos alimentarios en pacientes con SII. Se realizó una exploración bibliográfica en los motores de búsqueda PubMed, ScienceDirect y BVS. Se encontró que las personas con SII pueden presentar anormalidades en la microestructura cerebral y alteraciones en la red cerebro-intestino asociadas a una mayor duración de los síntomas gastrointestinales y el aumento de la comorbilidad afectiva. También se sugiere una relación en distintas vías entre el estrés, depresión y ansiedad, síntomas de SIII y cambios en los hábitos de alimentación. Todo lo anterior puede motivar prácticas de alimentación restrictivas, cambios en el apetito, subadecuación de nutrientes incluso en algunos casos por el mismo manejo nutricional y, en general, deterioro de la calidad de vida de las personas con SII. Se sugiere un manejo integral que no solo implique un manejo farmacológico para los síntomas de SII y los estados de ansiedad y depresión, sino que también incluya un manejo psicológico, manejo nutricional personalizado y recomendaciones de mejora de los estilos de vida como la práctica de actividad física y manejo del estrés.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Adriani A, Ribaldone DG, Astegiano M, Durazzo M, Saracco GM, Pellicano R. Irritable bowel syndrome: The clinical approach. Panminerva Med. 2018;60(4):213-22. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0031-0808.18.03541-3
Ford AC, Sperber AD, Corsetti M, Camilleri M. Irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet. 2020;396(10263):1675–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31548-8
Koloski N, Holtmann G, Talley NJ. Is there a causal link between psychological disorders and functional gastrointestinal disorders? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14(11):1047–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2020.1801414
Aziz MNM, Kumar J, Nawawi KNM, Ali RAR, Mokhtar NM. Irritable bowel syndrome, depression, and neurodegeneration: A bidirectional communication from gut to brain. Nutrients. 2021;13(9):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093061
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, Mcewen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: Advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5(4):371–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1123
Sucharew H, Macaluso M. Methods for research evidence synthesis: The scoping review approach. J Hosp Med. 2019;14(7):416–8. https://doi.org/10.12788/jhm.3248
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467–73. https://doi.org/10.7326/M18-0850
Luo M, Zhuang X, Tian Z, Xiong L. Alterations in short-chain fatty acids and serotonin in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021;21(1):14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-020-01577-
Long-Smith C, O’Riordan KJ, Clarke G, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Microbiota-gut-brain axis: New therapeutic opportunities. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020;60:477–502. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010919-023628
Hyland NP, Quigley EMM, Brint E. Microbiota-host interactions in irritable bowel syndrome: Epithelial barrier, immune regulation and brain-gut interactions. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(27):8859–66. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8859
Margolis KG, Cryan JF, Mayer EA. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(5):1486–501. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.066
Kennedy PJ, Clarke G, Quigley EMM, Groeger JA, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Gut memories: Towards a cognitive neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012;36(1):310–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.07.001
Pae CU, Masand PS, Ajwani N, Lee C, Patkar AA. Irritable bowel syndrome in psychiatric perspectives: A comprehensive review. Int J Clin Pract. 2007;61(10):1708–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01409.x
Buckley MM, O’Mahony SM, O’Malley D. Convergence of neuro-endocrine-immune pathways in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(27):8846–58. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8846
Qin HY, Cheng CW, Tang XD, Bian ZX. Impact of psychological stress on irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(39):14126–31. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14126
Bolino CM, Bercik P. Pathogenic Factors Involved in the Development of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Focus on a Microbial Role. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2010;24(4):961–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2010.07.005
Pellissier S, Bonaz B. The Place of Stress and Emotions in the Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Vitam Horm. 2017;103:327-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2016.09.005
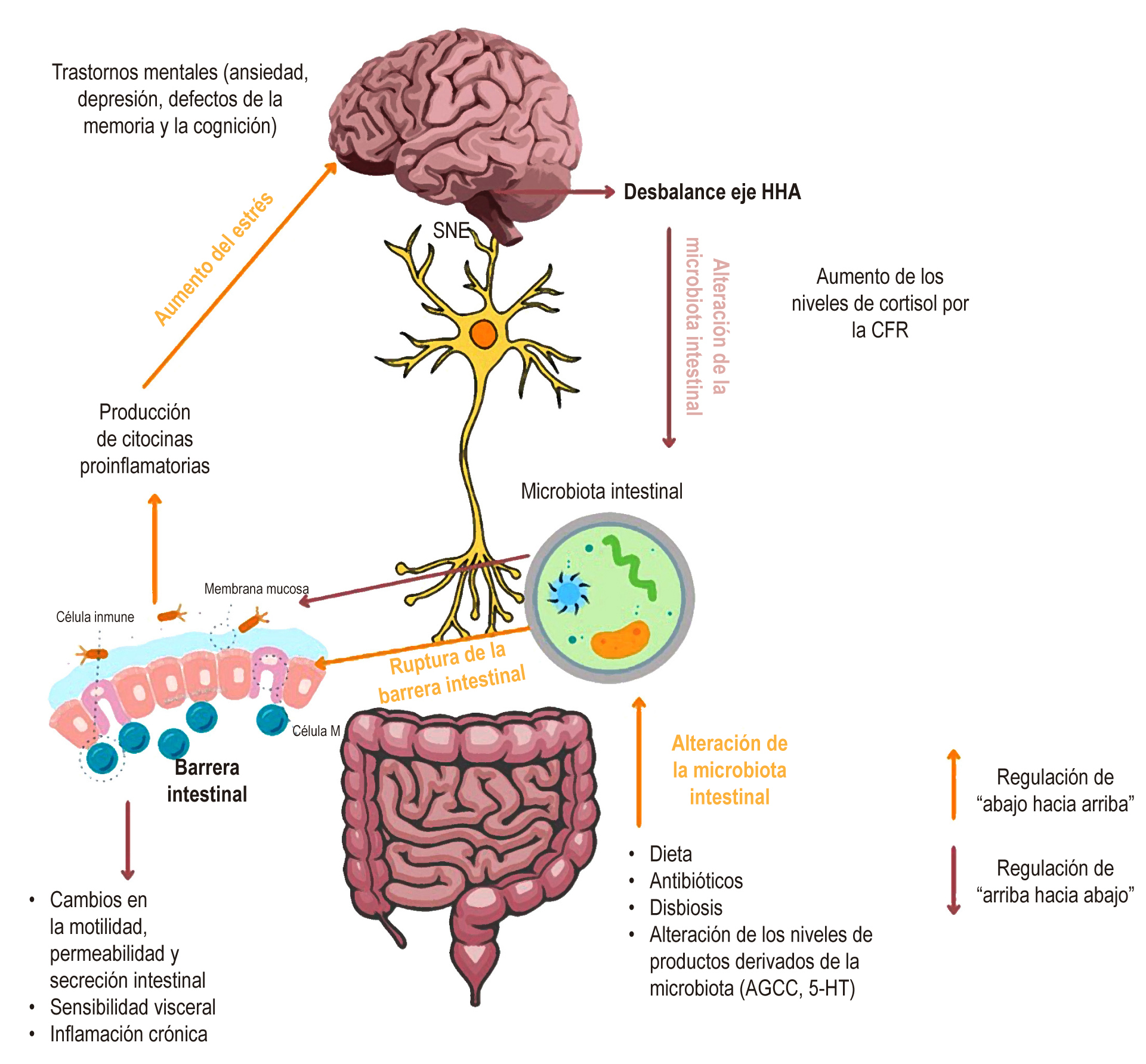
Osadchiy V, Martin CR, Mayer EA. The Gut-Brain Axis and the Microbiome: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(2):322-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.002
Labanski A, Langhorst J, Engler H, Elsenbruch S. Stress and the brain-gut axis in functional and chronic-inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases: A transdisciplinary challenge. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020;111:104501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104501
Tait C, Sayuk GS. The Brain-Gut-Microbiotal Axis: A framework for understanding functional GI illness and their therapeutic interventions. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;84:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2020.12.023
Koloski NA, Jones M, Talley NJ. Evidence that independent gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut pathways operate in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia: a 1-year population-based prospective study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;44(6):592–600. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13738
Surdea-Blaga T, Bằban A, Dumitrascu DL. Psychosocial determinants of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(7):616–26. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.616
Van Oudenhove L, Levy RL, Crowell MD, Drossman DA, Halpert AD, Keefer L, et al. Biopsychosocial aspects of functional gastrointestinal disorders: How central and environmental processes contribute to the development and expression of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1355-1367.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.027
Van Oudenhove L, Törnblom H, Störsrud S, Tack J, Simrén M. Depression and Somatization Are Associated with Increased Postprandial Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(4):866–74. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2015
Mudyanadzo TA, Hauzaree C, Yerokhina O, Architha NN, Ashqar HM. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Depression: A Shared Pathogenesis. Cureus. 2018;10(8):e3178. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.3178
Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Regulation of the stress response by the gut microbiota: Implications for psychoneuroendocrinology. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012;37(9):1369–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.03.007
Bazhan N, Zelena D. Food-intake regulation during stress by the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Brain Res Bull. 2013;95:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.04.002
Ans AH, Anjum I, Satija V, Inayat A, Asghar Z, Akram I, et al. Neurohormonal Regulation of Appetite and its Relationship with Stress: A Mini Literature Review. Cureus. 2018;10(7):e3032. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.3032
Simons M, Taft TH, Doerfler B, Ruddy JS, Bollipo S, Nightingale S, et al. Narrative review: Risk of eating disorders and nutritional deficiencies with dietary therapies for irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2022;34(1): e14188. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14188
Satherley R, Howard R, Higgs S. Disordered eating practices in gastrointestinal disorders. Appetite. 2014;84:240–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2014.10.006
Cuomo R, Andreozzi P, Zito FP, Passananti V, De Carlo G, Sarnelli G. Irritable bowel syndrome and food interaction. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(27):8837–45. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8837
Litleskare S, Wensaas KA, Eide GE, Hanevik K, Kahrs GE, Langeland N, et al. Perceived food intolerance and irritable bowel syndrome in a population 3 years after a giardiasis-outbreak: A historical cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015;15(1):164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-015-0393-0
Vakhshoori M, Saneei P, Esmaillzadeh A, Daghaghzadeh H, Hassanzadeh Keshteli A, Adibi P. The association between meal and snack frequency and irritable bowel syndrome. Public Health Nutr. 2021;24(13):4144–55. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980020002967
De Petrillo A, Hughes LD, McGuinness S, Roberts D, Godfrey E. A systematic review of psychological, clinical and psychosocial correlates of perceived food intolerance. J Psychosom Res. 2021;141:110344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110344
Melchior C, Algera J, Colomier E, Törnblom H, Simrén M, Störsrud S. Food Avoidance and Restriction in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Relevance for Symptoms, Quality of Life and Nutrient Intake. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(6):1290-1298.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.004
Hayes P, Corish C, O’Mahony E, Quigley EMM. A dietary survey of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2014;27 Suppl 2:36-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/jhn.12114
Böhn L, Störsrud S, Simrén M. Nutrient intake in patients with irritable bowel syndrome compared with the general population. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(1):23-30.e1. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12001
Alvarado J, Otero W, Jaramillo M, Roa P, Puentes G, Jimenez A, Grillo F, Pardo R, Sabbagh LC. Guía de práctica clínica para el diagnóstico y tratamiento del síndrome de intestino irritable en la población adulta. Revista. colomb. Gastroenterol. 2015;30(Suppl1):43-56.
Ferreira AI, Garrido M, Castro-Poças F. Irritable Bowel Syndrome: News from an Old Disorder. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2020;27(4):255–68. https://doi.org/10.1159/000503757
Guía de consulta de los criterios diagnósticos del DSM-5. Arlington, VA: Asociación Americana de Psiquiatría, 2013.
McGowan A, Harer KN. Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Eating Disorders: A Burgeoning Concern in Gastrointestinal Clinics. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2021;50(3):595–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2021.03.007
Mari A, Hosadurg D, Martin L, Zarate-Lopez N, Passananti V, Emmanuel A. Adherence with a low-FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome: Are eating disorders the missing link? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31(2):178–82. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000001317
Kayar Y, Agin M, Dertli R, Kurtulmus A, Boyraz RK, Onur NS, et al. Eating disorders in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;43(10):607–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastrohep.2020.03.001
Hanel V, Schalla MA, Stengel A. Irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia in patients with eating disorders - a systematic review. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2021;29(5):692–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/erv.2847
Akhondi N, Memar Montazerin S, Soltani S, Saneei P, Hassanzadeh Keshteli A, Esmaillzadeh A, et al. General and abdominal obesity in relation to the prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2019;31(4):e13549. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13549
Wang Y, Kasper LH. The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav Immun. 2014;38:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.015
Cryan JF, O’riordan KJ, Cowan CSM, Sandhu KV, Bastiaanssen TFS, Boehme M, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1877–2013. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
Malagelada JR. The Brain-Gut Team. Dig Dis. 2020;38(4):293–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505810
Slyepchenko A, Maes M, Jacka FN, Köhler CA, Barichello T, McIntyre RS, et al. Gut Microbiota, Bacterial Translocation, and Interactions with Diet: Pathophysiological Links between Major Depressive Disorder and Non-Communicable Medical Comorbidities. Psychother Psychosom. 2016;86(1):31–46. https://doi.org/10.1159/000448957
Pimentel M, Lembo A. Microbiome and Its Role in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65(3):829–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06109-5
Xiao L, Liu Q, Luo M, Xiong L. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:729346. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.729346
Sullivan EL, Riper KM, Lockard R, Valleau JC. Maternal High-Fat Diet Programming of the Neuroendocrine System and Behavior. Physiol Behav. 2012;43(2):145–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9384(88)90230-2
Rogers GB, Keating DJ, Young RL, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wesselingh S. From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: Mechanisms and pathways. Mol Psychiatry. 2016;21(6):738–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.50
Gaspar P, Cases O, Maroteaux L. The developmental role of serotonin: News from mouse molecular genetics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(12):1002–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1256
Ghaisas S, Maher J, Kanthasamy A. Gut microbiome in health and disease: Linking the microbiome-gut-brain axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;158:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.012
El-Salhy M, Gundersen D, Gilja OH, Hatlebakk JG, Hausken T. Is irritable bowel syndrome an organic disorder? World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(2):384–400. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.384
Zydecka KS-, Ka K. Gut Biofactory—Neurocompetent Metabolites within the Gastrointestinal Tract. A Scoping Review. Nutrients. 2020;12(11):3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113369
Mishima Y, Ishihara S. Enteric microbiota-mediated serotonergic signaling in pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910235
Tana C, Umesaki Y, Imaoka A, Handa T, Kanazawa M, Fukudo S. Altered profiles of intestinal microbiota and organic acids may be the origin of symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010;22(5) 512-9, e114-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01427.x
Farup PG, Rudi K, Hestad K. Faecal short-chain fatty acids - a diagnostic biomarker for irritable bowel syndrome? BMC Gastroenterol. 2016;16(1): 51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-016-0446-z
Spiller R. Serotonergic agents and the irritable bowel syndrome: what goes wrong? Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008;8(6):709–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2008.07.003
Park JM, Choi MG, Park JA, Oh JH, Cho YK, Lee IS, et al. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2006;18(11):995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2006.00829.x
Wang YM, Chang Y, Chang YY, Cheng J, Li J, Wang T, et al. Serotonin transporter gene promoter region polymorphisms and serotonin transporter expression in the colonic mucosa of irritable bowel syndrome patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24(6): :560-5, e254-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01902.x
Zhang ZF, Duan ZJ, Wang LX, Yang D, Zhao G, Zhang L. The serotonin transporter gene polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) and irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of 25 studies. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14: 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-14-23
Grzesiak M, Beszłej JA, Waszczuk E, Szechiński M, Szewczuk-Bogusławska M, Frydecka D, et al. Serotonin-related gene variants in patients with irritable bowel syndrome and depressive or anxiety disorders. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:4290430. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4290430
Keszthelyi D, Troost FJ, Jonkers DM, van Eijk HM, Dekker J, Buurman WA, et al. Visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome: Evidence for involvement of serotonin metabolism - a preliminary study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27(8):1127–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12600
Mujakovic S, ter Linde JJM, de Wit NJ, van Marrewijk CJ, Fransen GAJ, Onland-Moret NC, et al. Serotonin receptor 3A polymorphism c.-42C > T is associated with severe dyspepsia. BMC Med Genet. 2011;12:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-12-140
Weltens N, Iven J, Van Oudenhove L, Kano M. The gut–brain axis in health neuroscience: implications for functional gastrointestinal disorders and appetite regulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1428(1):129–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13969
de Weerth C. Do bacteria shape our development? Crosstalk between intestinal microbiota and HPA axis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2017;83:458–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2017.09.016
Bremner JD, Moazzami K, Wittbrodt MT, Nye JA, Lima BB, Gillespie CF, et al. Diet, stress and mental health. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082428
Irritable bowel syndrome in adults: diagnosis and management. Clinical guideline. Gastroenterology. NICE; 2008.
McKenzie YA, Bowyer RK, Leach H, Gulia P, Horobin J, O’Sullivan NA, et al. British Dietetic Association systematic review and evidence-based practice guidelines for the dietary management of irritable bowel syndrome in adults (2016 update). J Hum Nutr Diet. 2016;29(5):549–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/jhn.12385
Moayyedi P, Andrews CN, MacQueen G, Korownyk C, Marsiglio M, Graff L, et al. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). J Can Assoc Gastroenterol. 2019;2(1):6–29. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcag/gwy071
Settanni CR, Ianiro G, Ponziani FR, Bibbò S, Cammarota G, Gasbarrini A, et al. COVID-19 as a trigger of irritable bowel syndrome: A review of potential mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27(43):7433–45. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v27.i43.7433
Gill S, Adenan AM, Ali A. Living through the COVID-19 Pandemic : Impact and Lessons on Dietary Behavior and Physical Well-Being. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(2):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19020642
Remes-Troche JM, Coss-Adame E, Amieva-Balmori M, Velarde-Ruiz Velasco JA, Gómez-Castaños PC, Flores-Rendón R, et al. Incidence of “new-onset” constipation and associated factors during lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021;8(1):e000729. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2021-000729
Hod K, Ringel Y. Probiotics in functional bowel disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;30(1):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2016.01.003
Rodiño-Janeiro BK, Vicario M, Alonso-Cotoner C, Pascua-García R, Santos J. A Review of Microbiota and Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Future in Therapies. Adv Ther. 2018;35(3):289–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-018-0673-5
Ford AC, Quigley EMM, Lacy BE, Lembo AJ, Saito YA, Schiller LR, et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies, including hypnotherapy, in irritable bowel syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(9): 1350-65; quiz 1366. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2014.148
Lacy BE, Pimentel M, Brenner DM, Chey WD, Keefer LA, Long MD, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(1):17–44. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001036
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |