Surgical Management of Infected Pancreatic Necrosis. Case Series in a Quaternary Care Hospital in Bogotá, Colombia, 2014-2021
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.778Keywords:
Pancreatitis, Laparoscopy, Procalcitonin, Necrosis, APACHEAbstract
Introduction: Pancreatitis is a frequent pathology in our environment, mostly related to benign biliary pathology. It can progress to severe forms in 10-15 % of cases, where the pancreatic tissue becomes necrotic and forms large collections with risk of infection. We do not have epidemiological data about the incidence or management of this complication in Colombia.
Aim: This study aims to study the prevalence of infected pancreatic necrosis and describe the cases identified in a quaternary care hospital between 2014 and 2021.
Materials and methods: A cross-sectional observational study. We analyzed records of patients diagnosed with stage 2 pancreatitis. Those cases with infected pancreatic necrosis that underwent debridement plus laparoscopic and open surgical drainage at Hospital Universitario Mayor Méderi in Bogotá, Colombia, between January 2014 and January 2021 were studied. A convenience sampling was carried out without calculating the sample size. We collected the patients’ demographic and clinical variables, performing a descriptive statistical analysis in Excel. Qualitative variables were described through absolute and relative frequencies, while quantitative ones were expressed through measures of central tendency and dispersion based on their distribution.
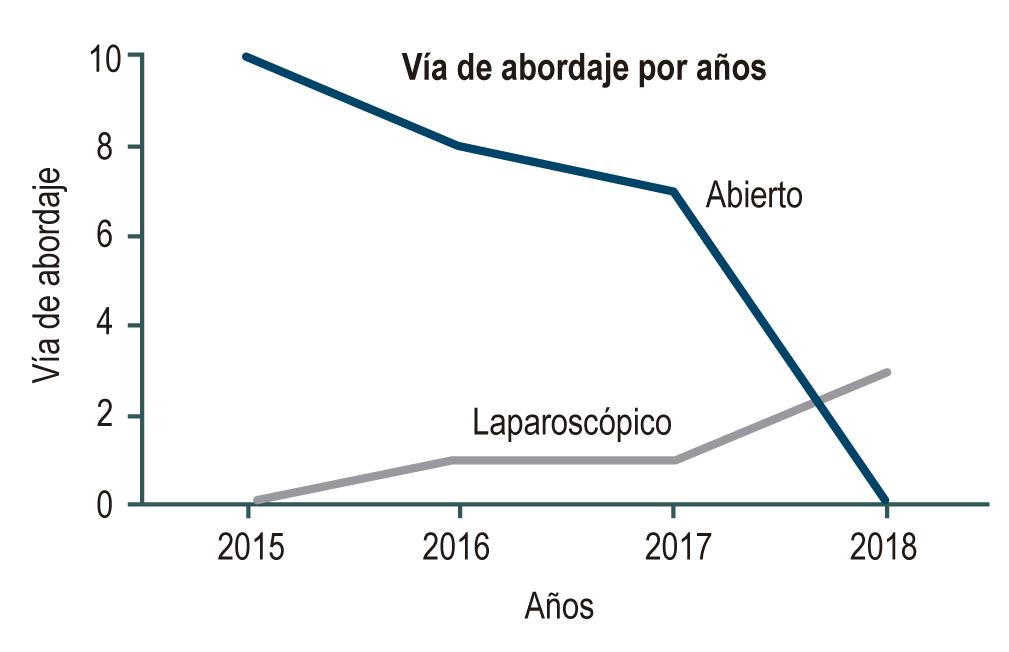
Results: We analyzed 1020 episodes of pancreatitis, finding pancreatic necrosis in 30 patients, i.e., a period prevalence of 2.9 %. Of the patients, 83 % (n = 25) underwent open drainage, with 48 % (n = 12) mortality. About laparoscopic management, the reduction in postoperative organ failure was 40 % (n = 2), with a 30 % shorter hospital stay than the open drainage approach. Those patients with a level of procalcitonin (PCT) lower than 1.8 ng/mL had less mortality.
Conclusions: The laparoscopic approach shows promising results regarding final morbidity and mortality.
Downloads
References
Senthil Kumar P, Ravichandran P, Jeswanth S. Case matched comparison study of the necrosectomy by retroperitoneal approach with transperitoneal approach for necrotizing pancreatitis in patients with CT severity score of 7 and above. Int J Surg. 2012;10(10):587-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2012.09.027
Tyberg A, Karia K, Gabr M, Desai A, Doshi R, Gaidhane M, et al. Management of pancreatic fluid collections: A comprehensive review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(7):2256-70. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i7.2256
Li A, Cao F, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X, Liu D, et al. Step-up mini-invasive surgery for infected pancreatic necrosis: Results from prospective cohort study. Pancreatology. 2016;16(4):508-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2016.03.014
Tu Y, Jiao H, Tan X, Sun L, Zhang W. Laparotomy versus retroperitoneal laparoscopy in debridement and drainage of retroperitoneal infected necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis. Surg Endosc. 2013;27(11):4217-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3026-0
Bouadma L, Luyt CE, Tubach F, Cracco C, Alvarez A, Schwebel C, et al. Use of procalcitonin to reduce patients’ exposure to antibiotics in intensive care units (PRORATA trial): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;375(9713):463-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61879-1
Mofidi R, Suttie SA, Patil PV, Ogston S, Parks RW. The value of procalcitonin at predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis and development of infected pancreatic necrosis: Systematic review. Surgery. 2009;146(1):72-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2009.02.013
Chen HZ, Ji L, Li L, Wang G, Bai XW, Cheng CD, et al. Early prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis secondary to necrotizing pancreatitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(30):e7487. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007487
de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, Girbes AR, Nijsten MW, de Lange DW. Procalcitonin to guide antibiotic stewardship in intensive care - Authors’ reply. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(8):889-90.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30210-9
Sarr MG, Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, et al. The new revised classification of acute pancreatitis 2012. Surg Clin North Am. 2013;93(3):549-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2013.02.012
Wroński M, Cebulski W, Witkowski B, Jankowski M, Kluciński A, Krasnodębski IW, et al. Comparison between minimally invasive and open surgical treatment in necrotizing pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 2017;210:22-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.10.022
Olakowski M, Dranka-Bojarowska D, Szlachta-Światkowska E, Lekstan A, Lampe P. Management of necrotizing pancreatitis: Flexible approach depending on intra-operative assessment of necrosis. Acta Chir Belg. 2006;106(2):172-6. https://doi.org/10.1080/00015458.2006.11679865
Schwender BJ, Gordon SR, Gardner TB. Risk factors for the development of intra-abdominal fungal infections in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2015;44(5):805-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000334
Götzinger P, Sautner T, Kriwanek S, Beckerhinn P, Barlan M, Armbruster C, et al. Surgical treatment for severe acute pancreatitis: Extent and surgical control of necrosis determine outcome. World J Surg. 2002;26(4):474-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-001-0252-8
van Baal MC, Bollen TL, Bakker OJ, van Goor H, Boermeester MA, Dejong CH, et al. The role of routine fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis of infected necrotizing pancreatitis. Surgery. 2014;155(3):442-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2013.10.001
Mowbray NG, Ben-Ismaeil B, Hammoda M, Shingler G, Al-Sarireh B. The microbiology of infected pancreatic necrosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2018;17(5):456-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2018.08.007
De Waele JJ, Rello J, Anzueto A, Moreno R, Lipman J, Sakr Y, et al. Infections and use of antibiotics in patients admitted for severe acute pancreatitis: Data from the epic II study. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2014;15(4):394-8. https://doi.org/10.1089/sur.2012.228
Mourad MM, Evans RPT, Kalidindi V, Navaratnam R, Dvorkin L, Bramhall SR. Prophylactic antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: Endless debate. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017;99(2):107-12. https://doi.org/10.1308/rcsann.2016.0355
John BJ, Swaminathan S, VenkataKrishnan L, Singh GS, Krishnaveni G, Mohandas N, et al. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis-the “step up” approach and minimal access retroperitoneal pancreatic necrosectomy. Indian J Surg. 2015;77(1):125-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-014-1197-0
Wolbrink DRJ, Kolwijck E, Ten Oever J, Horvath KD, Bouwense SAW, Schouten JA. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis in the intensive care unit: A narrative review. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(1):18-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.017
Roberts SE, Morrison-Rees S, John A, Williams JG, Brown TH, Samuel DG. The incidence and aetiology of acute pancreatitis across Europe. Pancreatology. 2017;17(2):155-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2017.01.005
Trikudanathan G, Wolbrink DRJ, van Santvoort HC, Mallery S, Freeman M, Besselink MG. Current concepts in severe acute and necrotizing pancreatitis: An evidence-based approach. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(7):1994-2007. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.269
van Santvoort HC, Bakker OJ, Bollen TL, Besselink MG, Ahmed Ali U, Schrijver AM, et al. A conservative and minimally invasive approach to necrotizing pancreatitis improves outcome. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(4):1254-63. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.073
Petrov MS, Chong V, Windsor JA. Infected pancreatic necrosis: Not necessarily a late event in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(27):3173-6. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i27.3173
Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Boermeester MA, Nieuwenhuijs VB, van Goor H, Dejong CH, et al. Timing and impact of infections in acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2009;96(3):267-73. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.6447
Buchler M, Malfertheiner P, Friess H, Isenmann R, Vanek E, Grimm H, et al. Human pancreatic tissue concentration of bactericidal antibiotics. Gastroenterology. 1992;103(6):1902-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(92)91450-i
Ullmann AJ, Aguado JM, Arikan-Akdagli S, Denning DW, Groll AH, Lagrou K, et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24(Suppl 1):e1-e38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2018.01.002
Kullberg BJ, Viscoli C, Pappas PG, Vazquez J, Ostrosky-Zeichner L, Rotstein C, et al. Isavuconazole versus caspofungin in the treatment of candidemia and other invasive candida infections: The ACTIVE trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;68(12):1981-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy827
de Jong E, van Oers JA, Beishuizen A, Vos P, Vermeijden WJ, Haas LE, et al. Efficacy and safety of procalcitonin guidance in reducing the duration of antibiotic treatment in critically ill patients: A randomised, controlled, open label trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(7):819-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00053-0
Maravi-Poma E, Gener J, Álvarez-Lerma F, Olaechea P, Blanco A, Dominguez Munoz JE, et al. Early antibiotic treatment (prophylaxis) of septic complications in severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A prospective, randomized, multicenter study comparing two regimens with imipenem-cilastatin. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29(11):1974e80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-1956-z
Akshintala VS, Saxena P, Zaheer A, Rana U, Hutfless SM, Lennon AM, et al. A comparative evaluation of outcomes of endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage for symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79(6):921-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2013.10.032
Mouli VP, Sreenivas V, Garg PK. Efficacy of conservative treatment, without necrosectomy, for infected pancreatic necrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(2):333-40.e2.
https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.004.e2
Schuts EC, Hulscher MEJL, Mouton JW, Verduin CM, Stuart JWTC, Overdiek HWPM, et al. Current evidence on hospital antimicrobial stewardship objectives: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16(7):847-856. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00065-7
Rodríguez JR, Razo AO, Targarona J, Thayer SP, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL, et al. Debridement and closed packing for sterile or infected necrotizing pancreatitis: Insights into indications and outcomes in 167 patients. Ann Surg. 2008;247(2):294-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815b6976
Fritz S, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Rossmanith F, Strobel O, Schneider L, et al. Bacterial translocation and infected pancreatic necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis derives from small bowel rather than from colon. Am J Surg. 2010;200(1):111-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.08.019
Moka P, Goswami P, Kapil A, Xess I, Sreenivas V, Saraya A. Impact of antibiotic-resistant bacterial and fungal infections in outcome of acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2018;47(4):489-94. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000001019
Da Costa DW, Boerma D, van Santvoort HC, Horvath KD, Werner J, Carter CR, et al. Staged multidisciplinary step-up management for necrotizing pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2014;101(1):e65-79. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.9346
Easler JJ, Zureikat A, Papachristou GI. An update on minimally invasive therapies for pancreatic necrosis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;6(6):745-53. https://doi.org/10.1586/egh.12.48
Flint RS, Windsor JA. The role of the intestine in pathophysiology and management of severe acute pancreatitis. HPB. 2003;5(2):69-85. https://doi.org/10.1080/13651820310001108
van Brunschot S, van Grinsven J, Voermans RP, Bakker OJ, Besselink MG, Boermeester MA, et al. Transluminal endoscopic step-up approach versus minimally invasive surgical step-up approach in patients with infected necrotizing pancreatitis (TENSION trial): Design and rationale of a randomized controlled multicenter trial [ISRCTN09786711]. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13:161. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-161
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis - 2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62(1):102-11. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779
Sing VK, Wu BU, Bollen TL, Repas K, Maurer R, Mortele KJ, et al. Early systemic inflammatory response syndrome is associated with severe acute pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7(11):1247-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2009.08.012
Baronia AK, Azim A, Ahmed A, Gurjar M, Marak RS, Yadav R, et al. Invasive candidiasis in severe acute pancreatitis: Experience from a tertiary care teaching hospital. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2017;21(1):40-5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.198325
Schmidt PN, Roug S, Hansen EF, Knudsen JD, Novovic S. Spectrum of microorganisms in infected walled-off pancreatic necrosis e impact on organ failure and mortality. Pancreatology. 2014;14(6):444-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.pan.2014.09.001
Dellinger EP, Tellado JM, Soto NE, Ashley SW, Barie PS, Dugernier T, et al. Early antibiotic treatment for severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Surg. 2007;245(5):674-83. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000250414.09255.84
Solomkin JS, Mazuski JE, Bradley JS, Rodvold KA, Goldstein EJ, Baron EJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of complicated intra-abdominal infection in adults and children: Guidelines by the Surgical Infection Society and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(2):133-64. https://doi.org/10.1086/649554
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.

| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |















