Drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts using luminal apposition metal stent (LAMS): Experience in two reference centers in Colombia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.948Keywords:
Endoscopic ultrasound, Interventional ultrasonography, Gastrointestinal endoscopy, Pancreatic pseudocyst, Pancreatitis, Apposing metal stentsAbstract
Introduction: Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided drainage and luminal-apposing metal stents (LAMS) are the options for managing symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts.
Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness and safety of LAMS for EUS-guided drainage of symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts in two referral centers in Colombia.
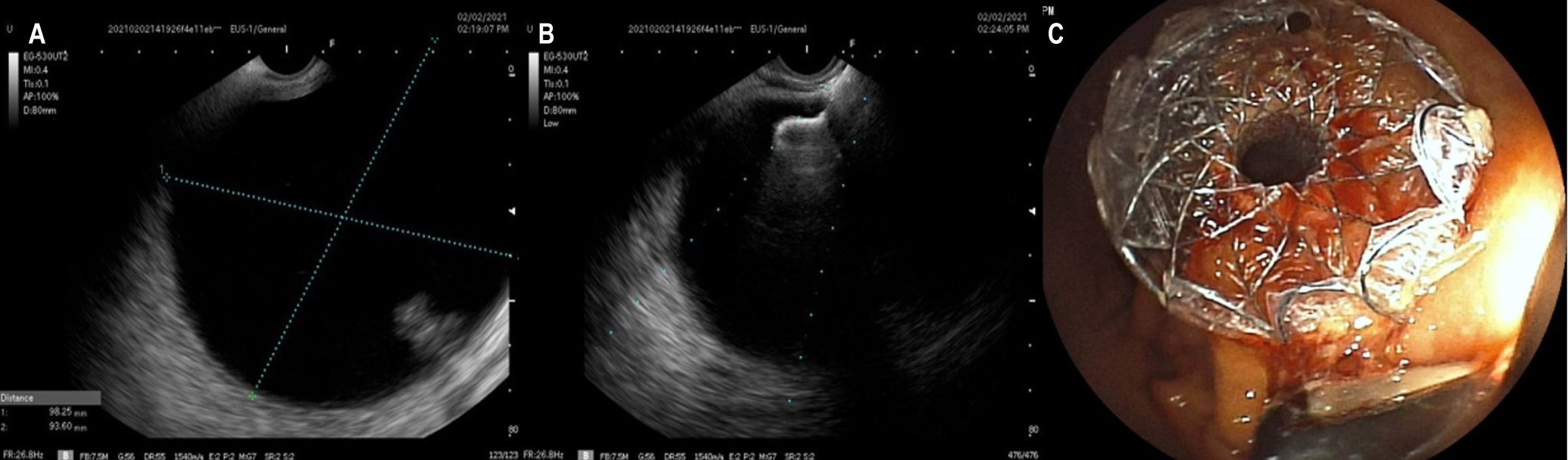
Materials and methods: A multicenter prospective cohort study between June 2019 and December 2021 included 13 patients diagnosed with symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts who underwent EUS-guided drainage with LAMS. Technical success, clinical success, and successful stent removal were evaluated as outcomes. Safety outcomes included stent-related adverse events and general adverse events. Follow-up was carried out for eight weeks, collecting data on stent removal.
Results: The average age was 53.4 years; 8/13 were men. The mean size of the pseudocyst was 9.56 ± 2.3 cm. Technical success was 100%, and clinical success was 92.3%. The stents were removed on average after 8 ± 2 weeks. The mean procedural time from puncture to stent deployment was 3.2 ± 2.4 minutes. In the imaging check-up, the collections had adequate drainage in all cases. There was a low frequency of complications; bleeding was documented in one case requiring surgery.
Conclusions: LAMS is safe and effective in managing symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts, reducing hospital stay and cost overruns. Clinical symptomatology prevails in the surgery decision.
Downloads
References
Law RJ, Chandrasekhara V, Bhatt A, Bucobo JC, Copland AP, Krishnan K, et al. Lumen-apposing metal stents (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;94(3):457-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2021.05.020
Giovannini M. Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Pancreatic Drainage. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2012;22(2):221-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giec.2012.04.004
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis - 2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013;62(1):102-11. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779
Chaves D, Mönkemüller K, Carneiro F, Medrado B, dos Santos M, Wodak S, et al. Endoscopic treatment of large pancreatic fluid collections (PFC) using self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) - a two-center experience. Endosc Int Open. 2014;2(4):E224-9.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1390796
Kahaleh M, Shami VM, Conaway MR, Tokar J, Rockoff T, De La Rue SA, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound drainage of pancreatic pseudocyst: A prospective comparison with conventional endoscopic drainage. Endoscopy. 2006;38(4):355-9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-925249
Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Tamhane A, Drelichman ER, Wilcox CM. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68(6):1102-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2008.04.028
Wrobel PS, Kaplan J, Siddiqui AA. A new lumen-apposing metal stent for endoscopic transluminal drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections. Endosc Ultrasound. 2014;3(4):203-4. https://doi.org/10.4103/2303-9027.144508
Hao S-J, Xu W-J, Di Y, Yao L, He H, Yang F, et al. Novel and supplementary management of pancreatic fluid collections: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;9(9):486-93. https://doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v9.i9.4869.
Mangiavillano B, Pagano N, Baron TH, Arena M, Iabichino G, Consolo P, et al. Biliary and pancreatic stenting: Devices and insertion techniques in therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasonography. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;8(3):143-56. https://doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i3.143
Siddiqui AA, Adler DG, Nieto J, Shah JN, Binmoeller KF, Kane S, et al. EUS-guided drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections and necrosis by using a novel lumen-apposing stent: A large retrospective, multicenter U.S. experience (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83(4):699-707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2015.10.020
Gómez Zuleta MA, Mindiola AL, Morales ÓFR. Case series of drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts guided by echoendoscopy without fluoroscopy . Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2017;32(2):160-5. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.143
Johnson MD, Walsh RM, Henderson JM, Brown N, Ponsky J, Dumot J, et al. Surgical versus nonsurgical management of pancreatic pseudocysts. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43(6):586-90. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e31817440be
Melman L, Azar R, Beddow K, Brunt LM, Halpin VJ, Eagon JC, et al. Primary and overall success rates for clinical outcomes after laparoscopic, endoscopic, and open pancreatic cystgastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc. 2009;23(2):267-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0196-2
Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Frequency of complications during EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections in 148 consecutive patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:1504-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06771.x
Patil R, Ona MA, Papafragkakis C, Anand S, Duddempudi S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided placement of axios stent for drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Ann Gastroenterol. 2016;29(2):168-73. https://doi.org/10.20524/aog.2016.0008
Yoo J, Yan L, Hasan R, Somalya S, Nieto J, Siddiqui AA. Feasibility, safety, and outcomes of a single-step endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections without fluoroscopy using a novel electrocautery-enhanced lumen-apposing, self-expanding metal stent. Endosc Ultrasound. 2017;6(2):131-5. https://doi.org/10.4103/2303-9027.204814
Shah RJ, Shah JN, Waxman I, Kowalski TE, Sanchez-Yague A, Nieto J, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections With Lumen-Apposing Covered Self-Expanding Metal Stents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:747-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.047
Akshintala VS, Saxena P, Zaheer A, Rana U, Hutfless SM, Lennon AM, et al. A comparative evaluation of outcomes of endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage for symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79(6):921-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2013.10.032
Siddiqui AA, Kowalski TE, Loren DE, Khalid A, Soomro A, Mazhar SM, et al. Fully covered self-expanding metal stents versus lumen-apposing fully covered self-expanding metal stent versus plastic stents for endoscopic drainage of pancreatic walled-off necrosis: clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(4):758-65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2016.08.014
Lang GD, Fritz C, Bhat T, Das KK, Murad FM, Early DS, et al. EUS-guided drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections with lumen-apposing metal stents and plastic double-pigtail stents: comparison of efficacy and adverse event rates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87(1):150-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2017.06.029
Umapathy C, Gajendran M, Mann R, Boregowda U, Theethira T, Elhanafi S, et al. Pancreatic fluid collections: Clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluation and management. Dis Mon. 2020;66(11):100986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disamonth.2020.100986
Nayar M, Leeds JS, Oppong K. Lumen-apposing metal stents for drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: does timing of removal matter? Gut. 2022;71(5):850-3. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325812
Bang JY, Navaneethan U, Hasan MK, Sutton B, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Non-superiority of lumen-apposing metal stents over plastic stents for drainage of walled-off necrosis in a randomised trial. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-315335
Tan S, Zhong C, Ren Y, Luo X, Xu J, Peng Y, et al. Are Lumen-Apposing Metal Stents More Effective Than Plastic Stents for the Management of Pancreatic Fluid Collections: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020;2020:4952721. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4952721
Barreto Noratto CP, Limas Solano LM. Drenaje de pseudoquiste pancreático gigante mediante cistogastrostomía endoscópica: reporte de caso. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2022;37(2):210-3. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.734
Sharaiha RZ, Tyberg A, Khashab MA, Kumta NA, Karia K, Nieto J, et al. Endoscopic Therapy With Lumen-apposing Metal Stents Is Safe and Effective for Patients With Pancreatic Walled-off Necrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(12):1797-803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2016.05.011
Whitworth PW, Holbert BL, Pawa R, Lalwani N, Tappouni R. The LACSEMS: what radiologists need to know. Abdom Radiol. 2019;44(3):976-83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-01904-9
Schawkat K, Luo M, Lee K, Beker K, Meir M, Berzin TM, et al. Lumen-apposing covered self-expanding metallic stent for symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections: assessment of outcomes and complications with CT and MRI. Abdom Radiol. 2021;46(2):757-67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02638-9
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














