Métodos diagnósticos en hipertensión portal
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.692Palabras clave:
Hipertensión portal, Sistema porta, Cirrosis hepáticaResumen
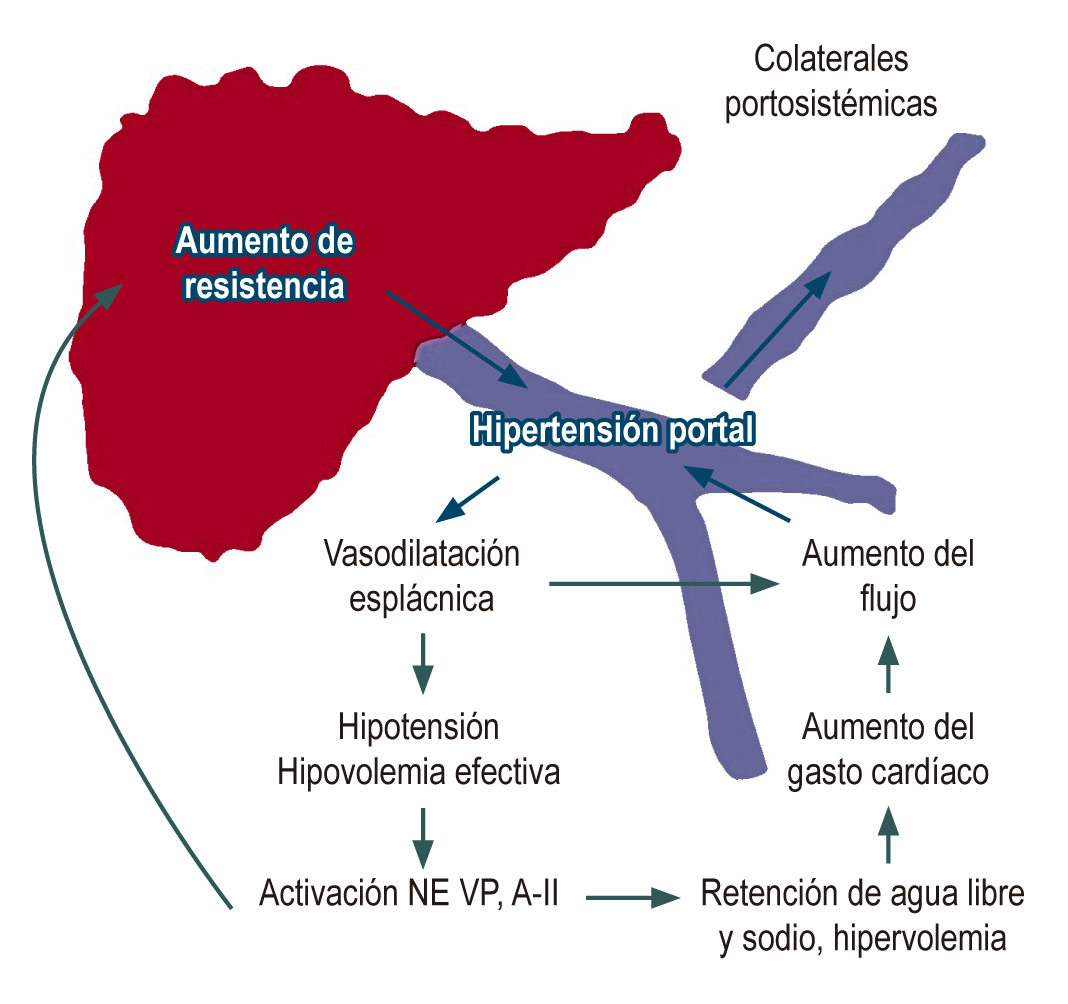
La hipertensión portal es un síndrome caracterizado por el incremento en el gradiente de presión portal, definido por la diferencia entre la presión de la porta y la vena cava inferior. Esta presión depende del flujo venoso y la resistencia vascular. En los pacientes cirróticos estas dos variables están alteradas de manera suprafisiológica, inicialmente por la lesión estructural dependiente de fibrosis y los nódulos de regeneración y posteriormente por cambios dinámicos vasculares que causan vasoconstricción intrahepática y vasodilatación esplácnica, lo cual explica las manifestaciones sistémicas de la cirrosis. La importancia de la hipertensión portal radica en la frecuencia y severidad de las complicaciones asociadas, especialmente la hemorragia variceal y otras como ascitis, peritonitis bacteriana espontanea, síndrome hepatorrenal y encefalopatía hepática. El objetivo de este artículo es realizar una revisión actualizada sobre el uso de las pruebas diagnósticas invasivas y no invasivas disponibles para el estudio de la hipertensión portal y su aplicación en la práctica clínica.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Reverter E, Bosch J. Assessing portal hypertension in liver diseases. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;7(2):141-55. https://doi.org/10.1586/egh.12.83
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, García-Pagan JC. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6(10):573-82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2009.149
Bosch J, García-Pagán JC. Complications of cirrhosis. I. Portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000;32(1 Suppl):141-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80422-5
Turco L, Garcia-Tsao G. Portal Hypertension: Pathogenesis and Diagnosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2019;23(4):573-587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2019.07.007
Tetangco EP, Silva RG, Lerma EV. Portal hypertension: Etiology, evaluation, and management. Dis Mon. 2016;62(12):411-426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disamonth.2016.08.001
Bosch J. Vascular deterioration in cirrhosis: the big picture. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;41 Suppl 3:S247-53. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181572357
Bloom S, Kemp W, Lubel J. Portal hypertension: pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Intern Med J. 2015;45(1):16-26. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.12590
García-Pagán JC, Gracia-Sancho J, Bosch J. Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2012;57(2):458-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007
Garcia-Tsao G, Groszmann RJ, Fisher RL, Conn HO, Atterbury CE, Glickman M. Portal pressure, presence of gastroesophageal varices and variceal bleeding. Hepatology. 1985;5(3):419-24. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840050313
Abraldes JG, Villanueva C, Bañares R, Aracil C, Catalina MV, Garci A-Pagán JC, et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient and prognosis in patients with acute variceal bleeding treated with pharmacologic and endoscopic therapy. J Hepatol. 2008;48(2):229-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2007.10.008
D'Amico G, Luca A. Natural history. Clinical-haemodynamic correlations. Prediction of the risk of bleeding. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997;11(2):243-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0950-3528(97)90038-5
Bosch J, Abraldes JG, Groszmann R. Current management of portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2003;38 Suppl 1:S54-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00430-0
Kapoor D, Sarin SK. Pathophysiology of portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;17 Suppl:S482-7. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1746.17.s4.14.x
Wu Y, Burns RC, Sitzmann JV. Effects of nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase inhibition on splanchnic hemodynamics in portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1993;18(6):1416-21.
Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, Epstein M, Henriksen JH, Rodés J. Peripheral arterial vasodilation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988;8(5):1151-7. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840080532
Simonetto DA, Liu M, Kamath PS. Portal Hypertension and Related Complications: Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(4):714-726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.12.020
Lautt WW, Greenway CV. Conceptual review of the hepatic vascular bed. Hepatology. 1987;7(5):952-63. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840070527
Pinzani M, Vizzutti F. Reversible factors in portal hypertension. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19:S155-S157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2004.03668.x
de Franchis R, Primignani M. Natural history of portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5(3):645-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70186-0
Westaby S, Wilkinson SP, Warren R, Williams R. Spleen size and portal hypertension in cirrhosis. Digestion. 1978;17(1):63-8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000198095
Abraldes JG, Angermayr B, Bosch J. The management of portal hypertension. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9(4):685-713, vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2005.08.001
Groszmann RJ, Wongcharatrawee S. The hepatic venous pressure gradient: anything worth doing should be done right. Hepatology. 2004;39(2):280-2. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20062
Karagiannakis DS, Voulgaris T, Siakavellas SI, Papatheodoridis GV, Vlachogiannakos J. Evaluation of portal hypertension in the cirrhotic patient: hepatic vein pressure gradient and beyond. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2018;53(10-11):1153-1164. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365521.2018.1506046
Moitinho E, Escorsell A, Bandi JC, Salmerón JM, García-Pagán JC, Rodés J, et al. Prognostic value of early measurements of portal pressure in acute variceal bleeding. Gastroenterology. 1999;117(3):626-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70455-5
Feu F, García-Pagán JC, Bosch J, Luca A, Terés J, Escorsell A, et al. Relation between portal pressure response to pharmacotherapy and risk of recurrent variceal haemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis. Lancet. 1995;346(8982):1056-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91740-3
Escorsell A, Bordas JM, Feu F, García-Pagán JC, Ginès A, Bosch J, et al. Endoscopic assessment of variceal volume and wall tension in cirrhotic patients: effects of pharmacological therapy. Gastroenterology. 1997;113(5):1640-6. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9352867
Idezuki Y. General rules for recording endoscopic findings of esophagogastric varices (1991). Japanese Society for Portal Hypertension. World J Surg. 1995;19(3):420-2; discussion 423. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00299178
Sarin SK, Agarwal SR. Gastric varices and portal hypertensive gastropathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5(3):727-67, x. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70190-2
De Palma GD, Rega M, Masone S, Persico F, Siciliano S, Patrone F, et al. Mucosal abnormalities of the small bowel in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: a capsule endoscopy study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;62(4):529-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(05)01588-9
Shah ND, Baron TH. Endoscopic ultrasound and the liver: current applications and beyond. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2018;25(3):171-180. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.528
Schiano TD, Adrain AL, Cassidy MJ, McCray W, Liu JB, Baranowski RJ, et al. Use of high-resolution endoluminal sonography to measure the radius and wall thickness of esophageal varices. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996;44(4):425-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(96)70093-7
Sung JJ, Lee YT, Leong RW. EUS in portal hypertension. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56(4 Suppl):S35-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-5107(02)70084-9
Obara K, Irisawa A, Sato Y. Usefulness of EUS in portal hypertension with esophageal varices. Digestive Endoscopy. y 2004;16(Suppl):S168-S172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1443-1661.2004.00432.x
Qamar AA, Grace ND, Groszmann RJ, Garcia-Tsao G, Bosch J, Burroughs AK, et al. Platelet count is not a predictor of the presence or development of gastroesophageal varices in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;47(1):153-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21941
Wongcharatrawee S, Groszmann RJ. Diagnosing portal hypertension. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2000;14(6):881-94. https://doi.org/10.1053/bega.2000.0136
Escorsell A, Garcia-Pagán JC, Bosch J. Assessment of portal hypertension in humans. Clin Liver Dis. 2001;5(3):575-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1089-3261(05)70182-3
Deng H, Qi X, Guo X. Diagnostic Accuracy of APRI, AAR, FIB-4, FI, King, Lok, Forns, and FibroIndex Scores in Predicting the Presence of Esophageal Varices in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(42):e1795. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001795
Hametner S, Ferlitsch A, Ferlitsch M, Etschmaier A, Schöfl R, Ziachehabi A, et al. The VITRO Score (Von Willebrand Factor Antigen/Thrombocyte Ratio) as a New Marker for Clinically Significant Portal Hypertension in Comparison to Other Non-Invasive Parameters of Fibrosis Including ELF Test. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0149230
Qi X, Berzigotti A, Cardenas A, Sarin SK. Emerging non-invasive approaches for diagnosis and monitoring of portal hypertension. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3(10):708-719. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30232-2
Sabbá C, Weltin GG, Cicchetti DV, Ferraioli G, Taylor KJ, Nakamura T, Moriyasu F, Groszmann RJ. Observer variability in echo-Doppler measurements of portal flow in cirrhotic patients and normal volunteers. Gastroenterology. 1990;98(6):1603-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(90)91097-p
Kamel IR, Liapi E, Fishman EK. Liver and biliary system: evaluation by multidetector CT. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43(6):977-97, vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcl.2005.07.003
Danrad R, Martin DR. MR imaging of diffuse liver diseases. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2005;13(2):277-93, vi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mric.2005.03.006
Roccarina D, Rosselli M, Genesca J, Tsochatzis EA. Elastography methods for the non-invasive assessment of portal hypertension. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;12(2):155-164. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2017.1374852
de Franchis R; Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2015;63(3):743-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022
Maurice JB, Brodkin E, Arnold F, Navaratnam A, Paine H, Khawar S, et al. Validation of the Baveno VI criteria to identify low risk cirrhotic patients not requiring endoscopic surveillance for varices. J Hepatol. 2016;65(5):899-905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.06.021
Colecchia A, Montrone L, Scaioli E, Bacchi-Reggiani ML, Colli A, Casazza G, et al. Measurement of spleen stiffness to evaluate portal hypertension and the presence of esophageal varices in patients with HCV-related cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):646-654. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.05.035
Berzigotti A, Seijo S, Arena U, Abraldes JG, Vizzutti F, García-Pagán JC, et al. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(1):102-111.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.001
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.

| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |